Back to Courses






Software Development Courses - Page 100
Showing results 991-1000 of 1266

Developing Android Apps with App Inventor
The course will give students hands-on experience in developing interesting Android applications. No previous experience in programming is needed, and the course is suitable for students with any level of computing experience. MIT App Inventor will be used in the course. It is a blocks-based programming tool that allows everyone, even novices, to start programming and build fully functional apps for Android devices. Students are encouraged to use their own Android devices for hands-on testing and exploitation.

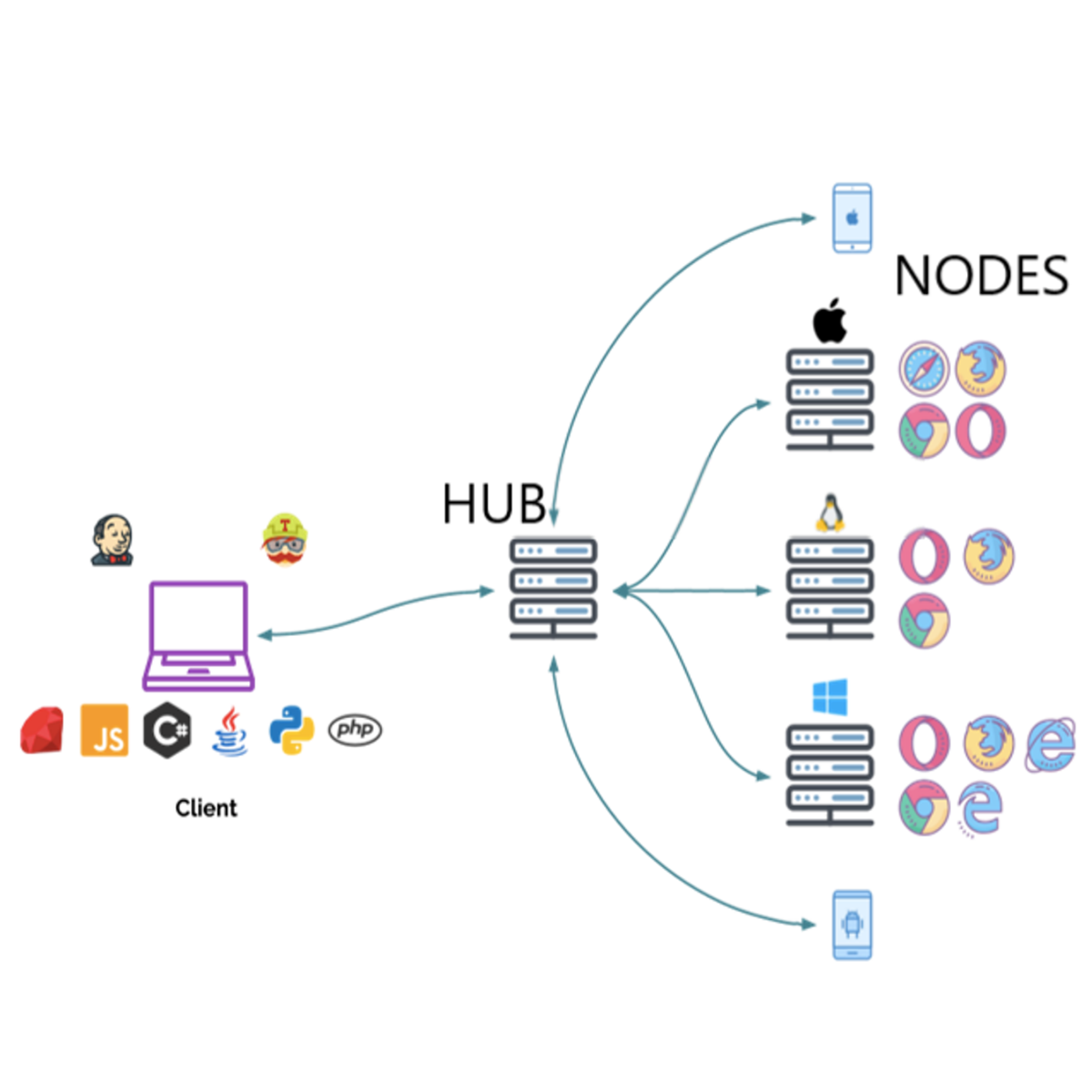
Selenium Grid - Running Selenium tests in parallel
“Selenium automates browser” That’s it! What you do with this power, is up to you!
Selenium Grid is one of the components of Selenium which allows users to run tests in parallel on multiple browsers, multiple operating systems, and machines.
Running Tests in parallel reduce the time and cost of execution of tests and results in better ROI.
Through hands-on, practical experience, you will go through concepts like Setting up Selenium Grid hub and node network and running Selenium tests parallelly on multiple browsers.

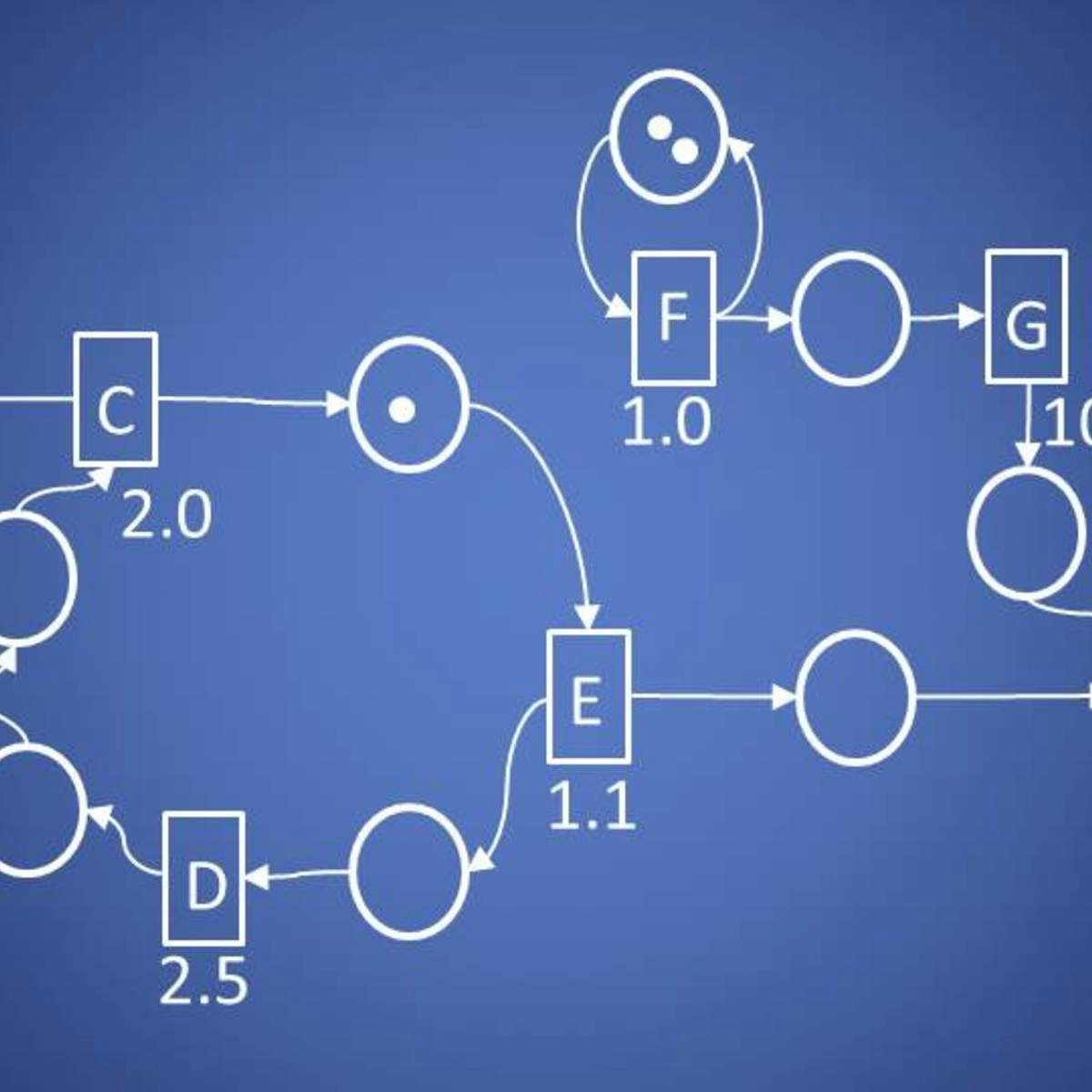
Quantitative Formal Modeling and Worst-Case Performance Analysis
Welcome to Quantitative Formal Modeling and Worst-Case Performance Analysis. In this course, you will learn about modeling and solving performance problems in a fashion popular in theoretical computer science, and generally train your abstract thinking skills.
After finishing this course, you have learned to think about the behavior of systems in terms of token production and consumption, and you are able to formalize this thinking mathematically in terms of prefix orders and counting functions. You have learned about Petri-nets, about timing, and about scheduling of token consumption/production systems, and for the special class of Petri-nets known as single-rate dataflow graphs, you will know how to perform a worst-case analysis of basic performance metrics, like throughput, latency and buffering.
Disclaimer: As you will notice, there is an abundance of small examples in this course, but at first sight there are not many industrial size systems being discussed. The reason for this is two-fold. Firstly, it is not my intention to teach you performance analysis skills up to the level of what you will need in industry. Rather, I would like to teach you to think about modeling and performance analysis in general and abstract terms, because that is what you will need to do whenever you encounter any performance analysis problem in the future. After all, abstract thinking is the most revered skill required for any academic-level job in any engineering discipline, and if you are able to phrase your problems mathematically, it will become easier for you to spot mistakes, to communicate your ideas with others, and you have already made a big step towards actually solving the problem. Secondly, although dataflow techniques are applicable and being used in industry, the subclass of single-rate dataflow is too restrictive to be of practical use in large modeling examples. The analysis principles of other dataflow techniques, however, are all based on single-rate dataflow. So this course is a good primer for any more advanced course on the topic.
This course is part of the university course on Quantitative Evaluation of Embedded Systems (QEES) as given in the Embedded Systems master curriculum of the EIT-Digital university, and of the Dutch 3TU consortium consisting of TU/e (Eindhoven), TUD (Delft) and UT (Twente). The course material is exactly the same as the first three weeks of QEES, but the examination of QEES is at a slightly higher level of difficulty, which cannot (yet) be obtained in an online course.

Real-World Cloud PM 2 of 3: Managing, Innovating, Pricing
Sponsored by AMAZON WEB SERVICES (AWS). Learn real-world technical and business skills for product managers or any job family involved in the rapidly expanding cloud computing industry. Ace the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam.
This course is the 2nd in a 3-course Specialization. Complete the first course before attempting this one.
Featuring
* NANCY WANG, GM of AWS Data Protection Services, AWS; Founder and CEO, Advancing Women in Tech (AWIT)
* GORDON YU, Technical Product Manager, AWS; General Counsel and Coursera Director, AWIT

Build a Guessing Game Application using C++
In this project you will create a guessing game application that pits the computer against the user. You will create variables, static methods, decision constructs, and loops in C++ to create the game.
C++ is a language developed to provide an Object-Oriented version of the C language. Learning C++ then gives the programmer a wide variety of career paths to choose from. It is used in many applications, from text editors to games to device drivers to Web Server code such as SQL Server. There is no more efficient higher level language than C, and C can be used within C++ code, since the C++ compiler supports C as well.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

IBM z/OS Rexx Programming
This course is designed to teach you the basic skills required to write programs using the REXX language in z/OS. The course covers the TSO extensions to REXX and interaction with other environments such as the MVS console, running REXX in batch jobs, and compiling REXX.
A total of 11 hands-on labs on an IBM Z server (via remote Skytap access) are part of this course.
On successful completion of the course, learners can earn theor badge. Details here- https://www.credly.com/org/ibm/badge/ibm-z-os-rexx-programming

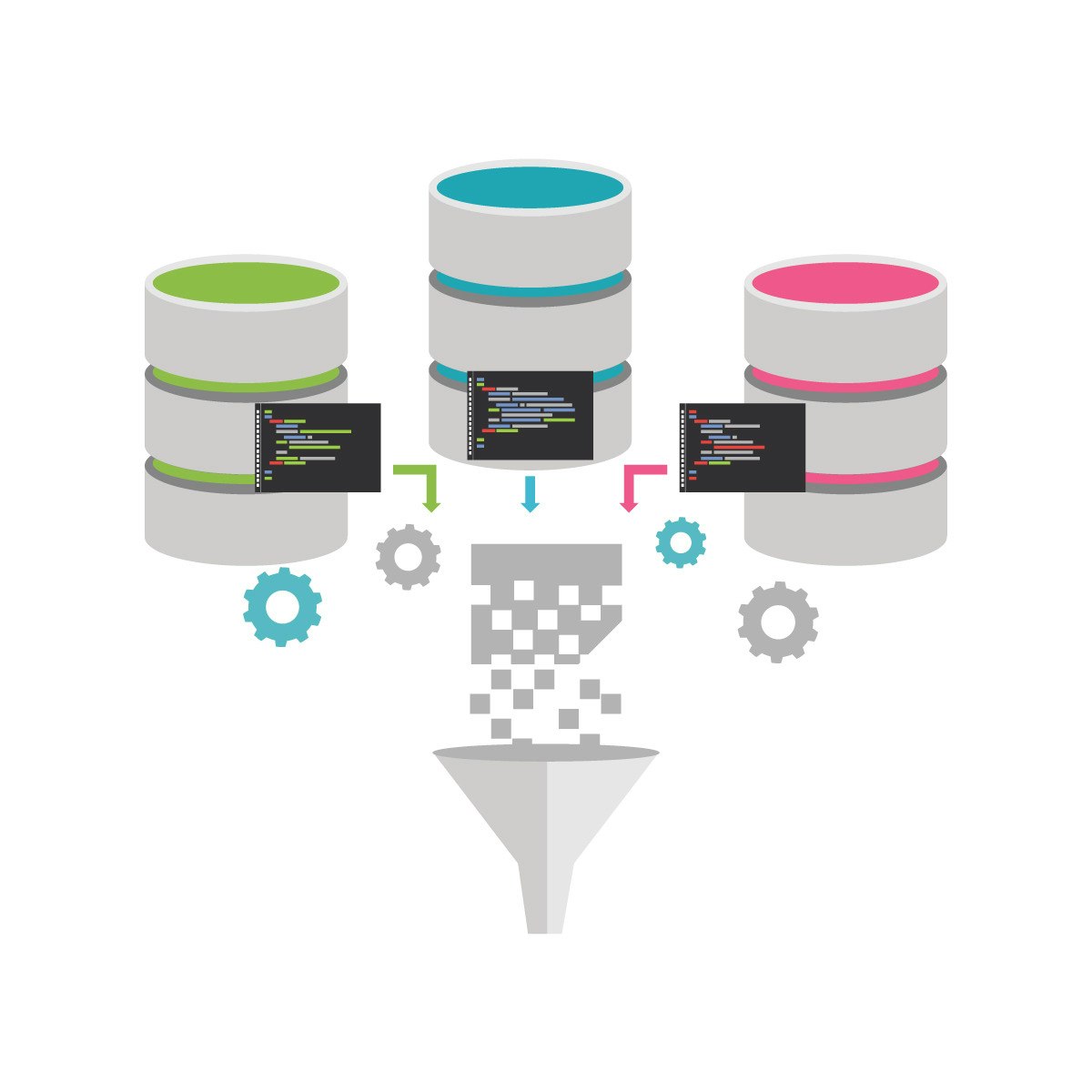
ETL and Data Pipelines with Shell, Airflow and Kafka
After taking this course, you will be able to describe two different approaches to converting raw data into analytics-ready data. One approach is the Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process. The other contrasting approach is the Extract, Load, and Transform (ELT) process. ETL processes apply to data warehouses and data marts. ELT processes apply to data lakes, where the data is transformed on demand by the requesting/calling application.
Both ETL and ELT extract data from source systems, move the data through the data pipeline, and store the data in destination systems. During this course, you will experience how ELT and ETL processing differ and identify use cases for both.
You will identify methods and tools used for extracting the data, merging extracted data either logically or physically, and for importing data into data repositories. You will also define transformations to apply to source data to make the data credible, contextual, and accessible to data users. You will be able to outline some of the multiple methods for loading data into the destination system, verifying data quality, monitoring load failures, and the use of recovery mechanisms in case of failure.
Finally, you will complete a shareable final project that enables you to demonstrate the skills you acquired in each module.

Performing Real Time Analytics with Stream Analytics
In this 1-hour long project-based course, you will learn how to (stream and process events with Azure Stream Analytics, data Ingestion with Event Hubs, processing data with Stream Analytics Jobs).
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Evaluating User Interfaces
In this course you will learn and practice several techniques for user interface evaluation. First we start with techniques that can be applied alone or in a design team, including action analysis, walkthroughs, and heuristic evaluation. Then we move on to user testing, including learning from a series of usability tests carried out in a real usability lab, and techniques to carry out your own tests even without a lab. Finally, we wrap up the discussion of evaluation--and of UI Design in the specialization as a whole--by looking at the question of how to set and measure usability goals, and in turn, when a design is usable enough to release it.

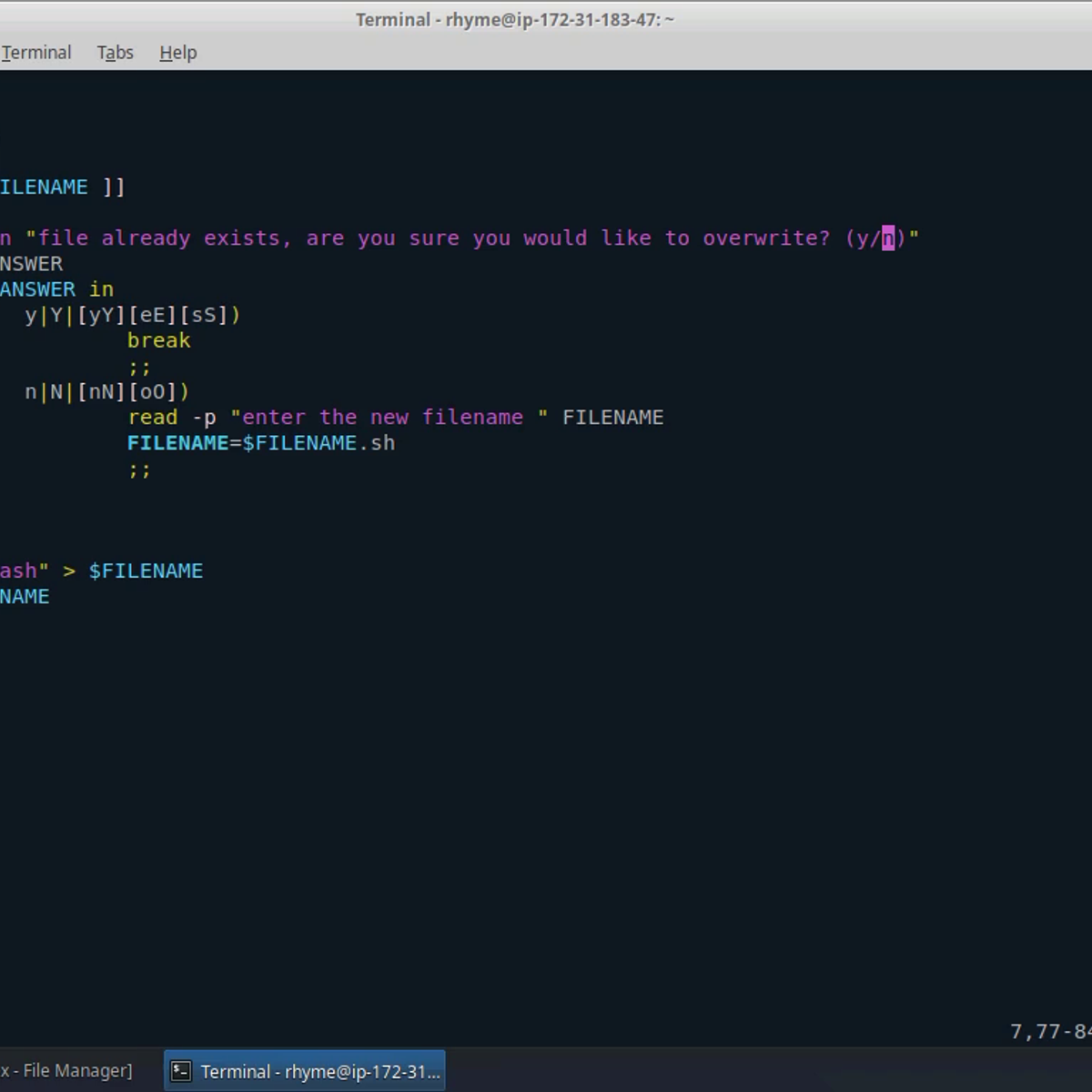
Automation Scripts Using Bash
In this 2-hour long project-based course, you will learn how to create Bash scripts that automates long and tedious tasks, evaluate and review some of the most commonly-used linux commands, and understand concepts such as conditional statements, loops, piping, and redirection to create powerful scripts.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved


