Back to Courses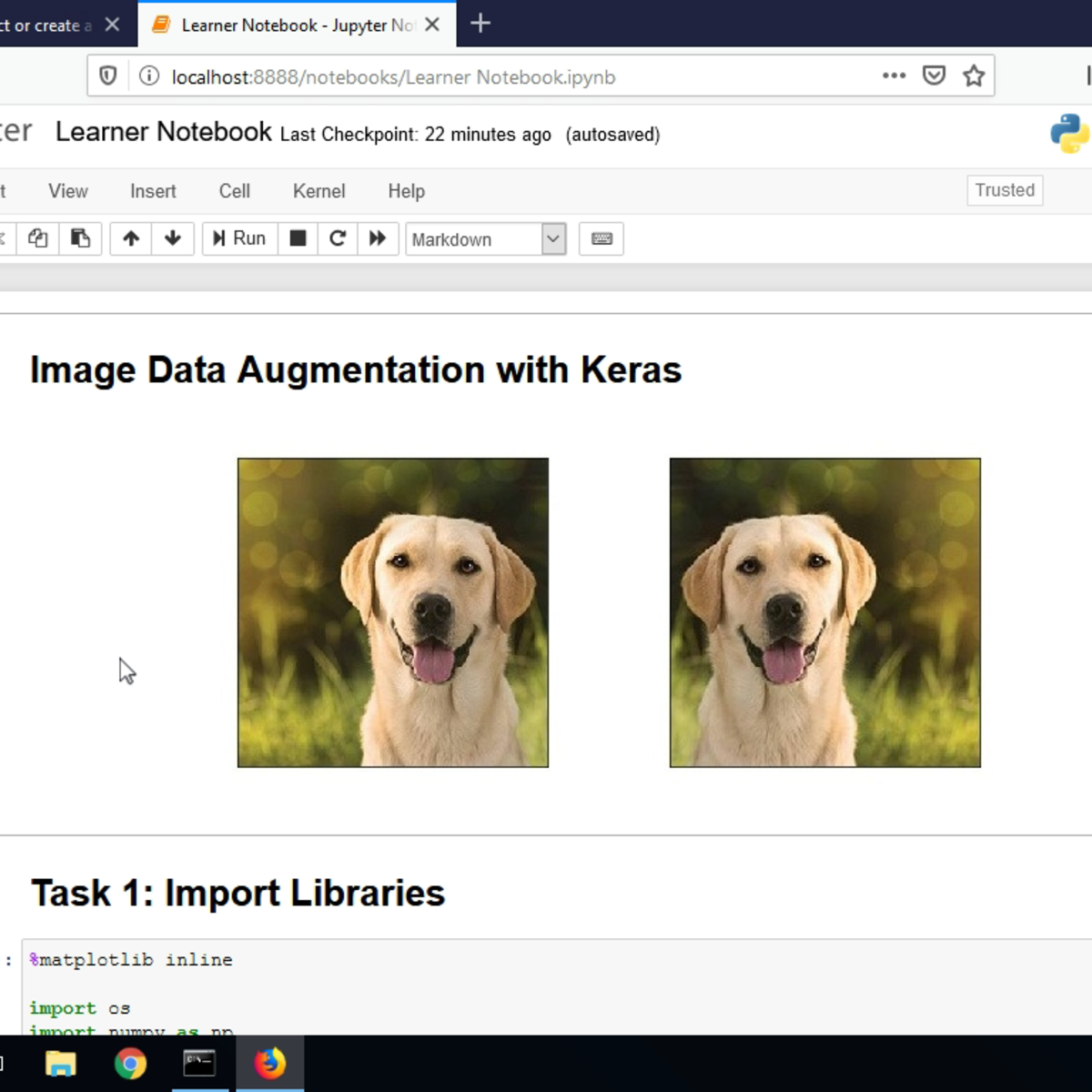






Algorithms Courses - Page 3
Showing results 21-30 of 326

Image Data Augmentation with Keras
In this 1.5-hour long project-based course, you will learn how to apply image data augmentation in Keras. We are going to focus on using the ImageDataGenerator class from Keras’ image preprocessing package, and will take a look at a variety of options available in this class for data augmentation and data normalization.
Since this is a practical, project-based course, you will need to prior experience with Python programming, convolutional neural networks, and Keras with a TensorFlow backend.
Data augmentation is a technique used to create more examples, artificially, from an existing dataset. This is useful if your dataset is small and you want to increase the number of examples. Data augmentation can often solve over-fitting so that your model generalizes well after training. For images, a variety of augmentation can be applied to increase the number of examples.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Discrete Optimization
Tired of solving Sudokus by hand? This class teaches you how to solve complex search problems with discrete optimization concepts and algorithms, including constraint programming, local search, and mixed-integer programming.
Optimization technology is ubiquitous in our society. It schedules planes and their crews, coordinates the production of steel, and organizes the transportation of iron ore from the mines to the ports. Optimization clears the day-ahead and real-time markets to deliver electricity to millions of people. It organizes kidney exchanges and cancer treatments and helps scientists understand the fundamental fabric of life, control complex chemical reactions, and design drugs that may benefit billions of individuals.
This class is an introduction to discrete optimization and exposes students to some of the most fundamental concepts and algorithms in the field. It covers constraint programming, local search, and mixed-integer programming from their foundations to their applications for complex practical problems in areas such as scheduling, vehicle routing, supply-chain optimization, and resource allocation.

Operations Research (3): Theory
Operations Research (OR) is a field in which people use mathematical and engineering methods to study optimization problems in Business and Management, Economics, Computer Science, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, etc.
The series of courses consists of three parts, we focus on deterministic optimization techniques, which is a major part of the field of OR.
As the third part of the series, we study mathematical properties of linear programs, integer programs, and nonlinear programs. We also introduce applications of these theoretical properties: How they help us develop better ways to solve mathematical programs.

Visualize the 10,000 Bitcoin Pizza Transaction Using BigQuery and AI Notebooks
This is a self-paced lab that takes place in the Google Cloud console. In this lab you will use an AI Platform Notebook instance to retrieve as many transactions as possible from BigQuery within 2 degrees of separation from the pizza exchange, post-process the transactions to remove excess transaction, then visualize the directed graph.

Create Ping-Pong Game in Python using Turtle Graphics
By the end of this project, you will be able to create The Classic Ping Pong game using Python and Turtle graphics. You’ll also be able to identify and use most of Turtle’s modules and functions that helps you develop and build your own game. Moreover, you’ll be able to edit and manipulate the objects created by Turtle however you like.
Turtle graphics is a pre-installed Python library that’s a trendy way of introducing programming to beginners. It helps visualize what programming can do. It’s a straightforward yet versatile way to understand the concepts of Python.
This guided project is for beginner-intermediate programmers who already have a general knowledge of Python basics and want to test out their knowledge with a real application and looking forward to developing their very first game in less than 1 hour. This project can be your portal into game development.
Note: This project works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Applying Data Structures to Manipulate Cleansed UN Data
In this 1-hour long project-based course, you will discover optimal situations to use fundamental data structures such as Arrays, Stacks, Queues, Hashtables, LinkedLists, and ArrayLists. By the end of this project you will create an application that processes an UN dataset, and manipulates this dataset using a variety of different data structures. In addition, you will explore how to implement each data structure using industry-standard Java practices, and gain experience manipulating real life data sets.
Data structures are an essential tool for any developer, and allow us to store and efficiently access data for even large datasets. Mastery of data structures allows your programs to be scalable and function without taking up too many system resources. We will use the Java Collections versions of each of these data structures, just as you would in real-life. Students can expect to walk away from the course confident in their ability to manipulate essential Java data structures, and have a working knowledge theory behind each data structure.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Classification with Transfer Learning in Keras
In this 1.5 hour long project-based course, you will learn to create and train a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with an existing CNN model architecture, and its pre-trained weights. We will use the MobileNet model architecture along with its weights trained on the popular ImageNet dataset. By using a model with pre-trained weights, and then training just the last layers on a new dataset, we can drastically reduce the training time required to fit the model to the new data . The pre-trained model has already learned to recognize thousands on simple and complex image features, and we are using its output as the input to the last layers that we are training.
In order to be successful in this project, you should be familiar with Python, Neural Networks, and CNNs.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Big Data Analysis Deep Dive
The job market for architects, engineers, and analytics professionals with Big Data expertise continues to increase. The Academy’s Big Data Career path focuses on the fundamental tools and techniques needed to pursue a career in Big Data.
This course includes: data processing with python, writing and reading SQL queries, transmitting data with MaxCompute, analyzing data with Quick BI, using Hive, Hadoop, and spark on E-MapReduce, and how to visualize data with data dashboards.
Work through our course material, learn different aspects of the Big Data field, and get certified as a Big Data Professional!

Battery Pack Balancing and Power Estimation
This course can also be taken for academic credit as ECEA 5734, part of CU Boulder’s Master of Science in Electrical Engineering degree.
In this course, you will learn how to design balancing systems and to compute remaining energy and available power for a battery pack. By the end of the course, you will be able to:
- Evaluate different design choices for cell balancing and articulate their relative merits
- Design component values for a simple passive balancing circuit
- Use provided Octave/MATLAB simulation tools to evaluate how quickly a battery pack must be balanced
- Compute remaining energy and available power using a simple cell model
- Use provided Octave/MATLAB script to compute available power using a comprehensive equivalent-circuit cell model

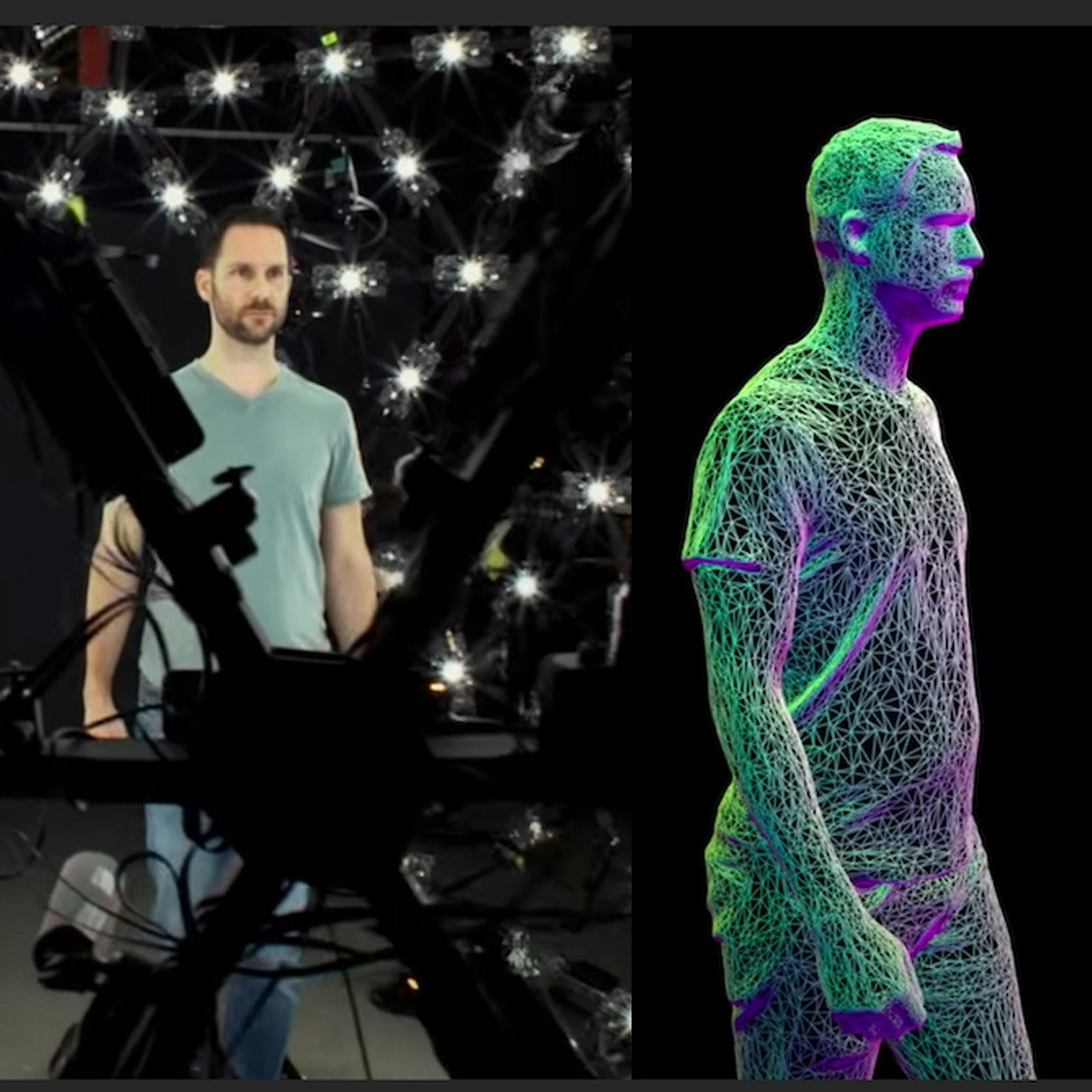
3D Reconstruction - Single Viewpoint
This course focuses on the recovery of the 3D structure of a scene from its 2D images. In particular, we are interested in the 3D reconstruction of a rigid scene from images taken by a stationary camera (same viewpoint). This problem is interesting as we want the multiple images of the scene to capture complementary information despite the fact that the scene is rigid and the camera is fixed. To this end, we explore several ways of capturing images where each image provides additional information about the scene.
In order to estimate scene properties (depth, surface orientation, material properties, etc.) we first define several important radiometric concepts, such as, light source intensity, surface illumination, surface brightness, image brightness and surface reflectance. Then, we tackle the challenging problem of shape from shading - recovering the shape of a surface from its shading in a single image. Next, we show that if multiple images of a scene of known reflectance are taken while changing the illumination direction, the surface normal at each scene point can be computed. This method, called photometric stereo, provides a dense surface normal map that can be integrated to obtain surface shape.
Next, we discuss depth from defocus, which uses the limited depth of field of the camera to estimate scene structure. From a small number of images taken by changing the focus setting of the lens, a dense depth of the scene is recovered. Finally, we present a suite of techniques that use active illumination (the projection of light patterns onto the scene) to get precise 3D reconstructions of the scene. These active illumination methods are the workhorse of factory automation. They are used on manufacturing lines to assemble products and inspect their visual quality. They are also extensively used in other domains such as driverless cars, robotics, surveillance, medical imaging and special effects in movies.
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Find Jobs & Internships
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved