Back to Courses








Arts And Humanities Courses - Page 25
Showing results 241-250 of 464

William Shakespeare's Romeo & Juliet: An Actor's Perspective
Have you ever wanted to read Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet? This course will provide a guided reading of the script and expose you to the perspectives of actors who've performed in the play. It primarily consists of interviews with 14 professional actors who have participated in at least one production of Romeo & Juliet somewhere in the US, at theaters and Shakespeare festivals including the American Shakespeare Center, American Players Theatre, and the Arkansas, Colorado, Illinois, New Jersey, and Utah Shakespeare Festivals.
In completing this course, learners will be able to describe the plot of Romeo & Juliet, identify major characters and themes, analyze and interpret heightened text, and consider multiple theatrical approaches to the play.
This course strives to be of interest to multiple audiences, but we think it may particularly appeal to...
* Shakespeare enthusiasts and the Shakespeare curious in all walks of life
* Actors, theater practitioners, and teachers of Shakespeare everywhere
* Secondary school and college students interested in expanding their studies of Shakespeare
* Interested readers with little or no familiarity with Shakespeare
Logo image courtesy of https://picryl.com/media/romeo-and-juliet-12

Journey Conversations: Weaving Knowledge and Action
Journey of the Universe weaves together the discoveries of the evolutionary sciences together with humanities such as history, philosophy, art, and religion. This course draws on the Journey of the Universe Conversations, a series of 20 interviews with scientists and environmentalists. The first 10 interviews are with scientists and historians who deepen our understanding of the evolutionary process of universe, Earth, and humans. The second 10 interviews are with environmentalists, teachers, and artists who explore the connections between the universe story and the practices for a flourishing Earth community.

Master Lighting in Inkscape
By the end of this project, you’ll be able to control lighting and highlights for objects in Inkscape. Inkscape, a free and open-source vector graphics program, offers built-in tools that help you render objects with stylized or realistic lighting effects. Adding light means adding depth and dimension, and it can be surprising how much life an object can have once light effects are applied.
To master lighting in Inkscape, you’ll practice with vector graphics tools and use three different methods to light up selected objects in Inkscape.
You’ll start with a quick examination of light and how it works, then use those ideas to build better lighting with filters, complex shapes, and gradients. By the end of the project, you’ll create a sample of what each method looks like.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Social Norms, Social Change I
This is a course on social norms, the rules that glue societies together. It teaches how to diagnose social norms, and how to distinguish them from other social constructs, like customs or conventions. These distinctions are crucial for effective policy interventions aimed to create new, beneficial norms or eliminate harmful ones. The course teaches how to measure social norms and the expectations that support them, and how to decide whether they cause specific behaviors. The course is a joint Penn-UNICEF project, and it includes many examples of norms that sustain behaviors like child marriage, gender violence and sanitation practices.
This is Part 1 of the Social Norms, Social Change series. In these lectures, I introduce all the basic concepts and definitions, such as social expectations and conditional preferences, that help us distinguish between different types of social practices like customs, descriptive norms and social norms. Expectations and preferences can be measured, and these lectures explain how to measure them. Measurement is crucial to understanding the nature of the practice you are facing, as well as whether an intervention was or was not successful, and why. In Part 2, we will put into practice all we have learned in Part 1.
New! Please use this link for a 30% discount on the recommended book that accompanies this course!
https://global.oup.com/academic/product/9780190622053/?cc=us&lang=en&promocode=AAFLYG6

Question Reality: Cosmos
This course explores the concept of reality and the physics of the sky. You will travel through the philosophies and worldviews of early civilizations to the time of early scientists such as Plato, Aristotle, and Copernicus.
You will learn how Galileo's findings with the telescope challenged the Aristotelian interpretation of the cosmos, about Galileo’s revolutionary conclusions on gravity, and Newton's universal law of gravitation.
This course will also introduce you to the scientific methods and their limitations. You will also explore the properties and behaviors of homemade pendulums.
Next, you will explore modern ideas of cosmology, of the Big Bang, and even recent speculations that our universe is not all there is. Mysteries and properties of light and how they were discovered, questioned, and confirmed through experiments over the past few hundred years through the present will also be discussed.

South Asian Religions & Ecology
At first glance the fields of religion and ecology may seem and unlikely pairing, but a deeper consideration reveals the two have a great deal to contribute to one another and are indeed inextricably linked. Religions recognize the unity and interdependence of humans with nature. Ecological sciences affirm this deep interconnection with the natural world. This partnership can inspire work for the wellbeing of the Earth community
There is a need for broader literacy and deeper knowledge of the world’s religions and their ecological contributions. This specialization, "Religions and Ecology: Restoring the Earth Community", contributes such a perspective. Each course celebrates the vitality of religiously-informed action for the Earth and recognizes the longstanding contributions of Indigenous peoples in offering visions and practices for ecological flourishing.
This course is part 3 of 5 of the "Religions and Ecology: Restoring the Earth Community" specialization that focuses on the ecological dimensions of religious traditions throughout the world.
The course you are about to begin is designed as a gateway to these aspects of the South Asian religions, philosophies, and practices of Hinduism, Jainism, Yoga, Buddhism, Sikhism, and Baha’i Faith. So much has emerged in the last several decades in this area, as you will see. While we have taught this course at Yale, we have adapted it for learners from a wide range of backgrounds.
This course is for lifelong learners curious to know more about world religions and ecology, environmental professionals eager to deepen the discourse of environmental protection and conservation, those working with non-profit organizations and NGOs on issues of ecological justice, and religion leaders and laity who wish to know how they can contribute to interreligious dialogue on environmental projects.

Approaching Music Theory: Melodic Forms and Simple Harmony
This course is about how music works. It is about the relationship between the technical and aesthetic details of music. It is also about how developing a meaningful theoretical vocabulary can help you think and talk about musical style, and how learning that vocabulary can expand your appreciation for music.
In this course you will learn music theory not by looking at theory itself, but by listening to, looking at, and—yes!—writing your own musical examples. By hearing, seeing, and writing yourself, you will learn about classical, modern, ancient, pop, jazz, and folk styles.
Through lectures, relevant examples, and numerous practice assignments, we will examine fundamental aspects of melody. We will move into working with two voices and counterpoint, and finally to three voices and the beginnings of harmonic function.
This is an intermediate-level course for musicians and composers who already have some understanding of music theory through previous study. If you are a musician or composer looking to build a deeper understanding of music theory for composing, performing, or improvisation, you have come to the right place. If you are an amateur lover of music or, perhaps, play a musical instrument and want to develop a deeper sense of appreciation for music theory, aesthetics, and history, you are also in the right place!

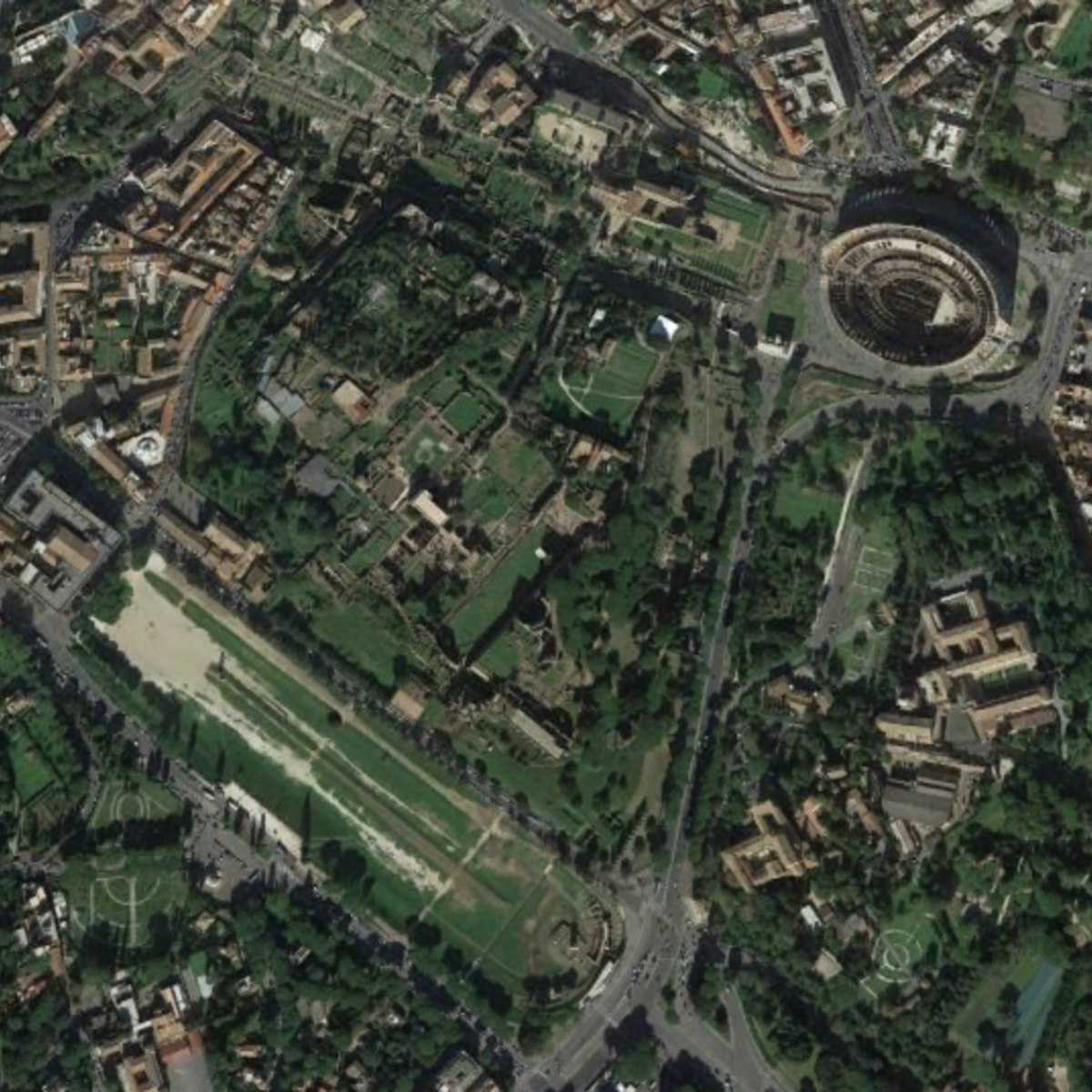
The Changing Landscape of Ancient Rome. Archaeology and History of the Palatine Hill
Studying ancient - as well as medieval or modern - cities basically means telling local urban stories based on the reconstruction of changing landscapes through the centuries. Given the fragmentary nature of archaeological evidence, it is necessary to create new images that would give back the physical aspect of the urban landscape and that would bring it to life again. We are not just content with analyzing the many elements still visible of the ancient city. The connections between objects and architectures, visible and non visible buildings, which have been broken through time have to be rejoined, to acknowledge the elements that compose the urban landscape.
Landscape and its content are a very relevant and still vital part of any national cultural heritage. The course will introduce students to the way we have been reflecting on over the last twenty years and still are engaged with the study of the past of our cities, beginning from the most complex case in the ancient Mediterranean World: the core of Italy and of Roman Empire. On the other hand, knowledge means also preservation and defense of material remains and cultural memory.
“The Changing Landscape of Ancient Rome. Archeology and History of the Palatine Hill” presents to a large public the topographical lay-out of the most relevant part of the city (according the Greek and Roman Historians Rome was founded on the Palatine). Research developed on the Palatine since the end of last century by the team of Sapienza Classical Archaeologists opened a new phase in the urban archaeological investigation and in the scientific debate about the relation between archaeological features and literary tradition as well as the “correct use“ of both kind of evidence, key issues of wide archaeological and historical significance.

Philosophy of Science
For the last four centuries, scientists have aimed to provide us with an understanding of the world around us. By all appearances, science has made substantial progress during this time. But is this progress real or illusory? And if it is real, how has this progress been made? This four-week course will consider these important questions. Specific topics will include how scientists generate knowledge through observations, experiments, and simulations; scientific objectivity and failures of scientific objectivity; the self-correcting nature of the scientific community; the positive and negative influences that values can have on science; the relationship between science and religion; and the role of the public in guiding the scientific enterprise.

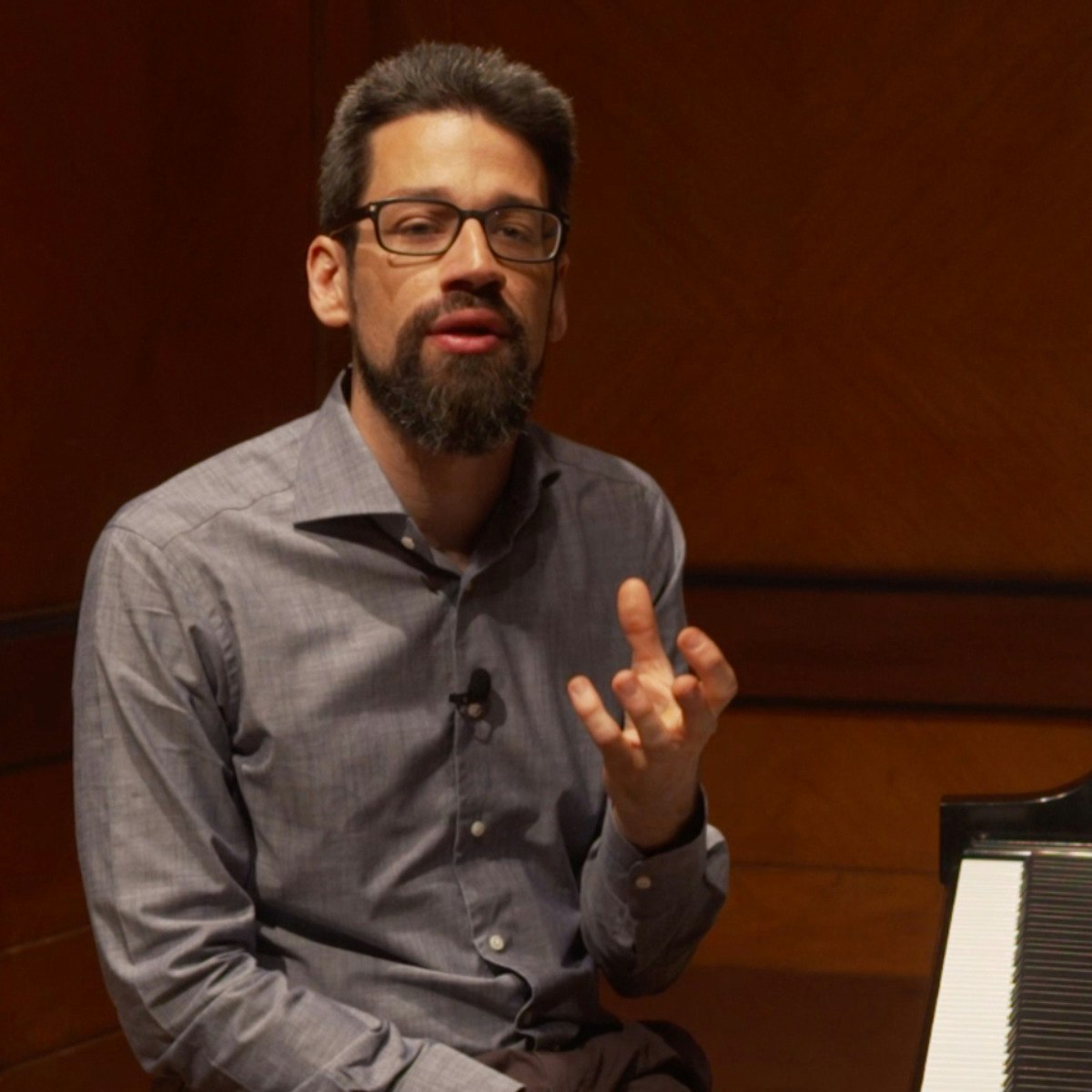
Exploring Beethoven's Piano Sonatas Part 4
Please join us for Part 4 of Exploring Beethoven's Piano Sonatas course, taught by Curtis faculty member and extraordinary concert artist, Jonathan Biss. This course is new and contains separate sets of lectures and sonatas that we not previously discussed. Specifically, in Part 4, we will cover Beethoven's Piano Sonatas Op. 2, No. 2, Op. 10, No. 3, Op. 28 and Op. 110. As with the other three Beethoven courses, it is not necessary to have taken the previous Exploring Beethoven's Piano Sonatas courses. We think you will be perfectly comfortable to start learning with Part 4, if you wish and go from here. There is always the option to go back to earlier parts at any time. Between these courses, there exists a large amount of additional resources and learning that might be helpful as you embark on Part 4. We certainly encourage you to take Parts 1, 2 and 3, if you have not yet. In the meantime, enjoy the class and Part 4 of Exploring Beethoven’s Piano Sonatas.
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Find Jobs & Internships
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved