Back to Courses





Algorithms Courses - Page 18
Showing results 171-180 of 326

Jet Fighters Game using Pygame
By the end of this project, you will create a fully functioning 2 player jet fighters game using Pygame in Microsoft Visual Studio Code. This project will give you a great head start towards learning more and mastering one of the most used programming languages in the world. In this project you will be able to identify and apply many basic fundamentals such as data structures, variables, loops etc. and create a GUI with dynamic labels and dynamic objects. Learning and understanding Pygame in Python will help you progress in the programming field by creating simple Python applications.

Computer Science: Programming with a Purpose
The basis for education in the last millennium was “reading, writing, and arithmetic;” now it is reading, writing, and computing. Learning to program is an essential part of the education of every student, not just in the sciences and engineering, but in the arts, social sciences, and humanities, as well. Beyond direct applications, it is the first step in understanding the nature of computer science’s undeniable impact on the modern world. This course covers the first half of our book Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach (the second half is covered in our Coursera course Computer Science: Algorithms, Theory, and Machines). Our intent is to teach programming to those who need or want to learn it, in a scientific context.
We begin by introducing basic programming elements such as variables, conditionals, loops, arrays, and I/O. Next, we turn to functions, introducing key concepts such as recursion, modular programming, and code reuse. Then, we present a modern introduction to object-oriented programming.
We use the Java programming language and teach basic skills for computational problem solving that are applicable in many modern computing environments. Proficiency in Java is a goal, but we focus on fundamental concepts in programming, not Java per se.
All the features of this course are available for free. It does not offer a certificate upon completion.

Create C# App Inheritance, Composition, and Aggregation
By the end of this project you will create an application that uses the C# List data structure and the C# Linq to process a collection of Employees in a file.
Linq, when used with the List data structure, allows the programmer to compare and perform computations on objects without the need to access attributes directly. It simplifies the process of iterating through a list and obtaining data from user-defined objects.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.
Getting Started with AI using IBM Watson
In this course you will learn how to quickly and easily get started with Artificial Intelligence using IBM Watson. You will understand how Watson works, become familiar with its use cases and real life client examples, and be introduced to several of Watson AI services from IBM that enable anyone to easily apply AI and build smart apps. You will also work with several Watson services to demonstrate AI in action.
This course does not require any programming or computer science expertise and is designed for anyone whether you have a technical background or not.

Statistical Analysis using Python Numpy
By the end of this project you will use the statistical capabilities of the Python Numpy package and other packages to find the statistical significance of student test data from two student groups.
The T-Test is well known in the field of statistics. It is used to test a hypothesis using a set of data sampled from the population. To perform the T-Test, the population sample size, the mean, or average, of each population, and the standard deviation are all required. These will all be calculated in this project.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Conducting Exploratory Data Analysis
Conduct exploratory data analysis with a systematic approach to investigate different aspects of your data: comparisons, relationships, compositions, and distributions. This guided project gives you a framework so you can conduct your own exploratory data analysis and make your work more professional and organized. The language is Python and the libraries used are seaborn, pandas, and matplotlib.

Add and Modify Records with COBOL
In this project you will learn to process data records in a sequential file using COBOL. You will code, compile, and run programs that add new records to an existing file and modify individual data values on existing file records. Your hands-on practice will take place in the PC-based OpenCobolIDE application.

Create a Dynamic-Link Library with DevC++ for Python
By the end of this project you will implement a function using C that raises each element of an array to a given power and then call the function using the Python ctypes package.
The C programming language is the basis for many other programming languages. Its performance cannot be matched in any other language. Python is known for its simplicity, allowing the programmer to focus on the application. Sometimes it is useful to take advantage of the speed of C in a Python application.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

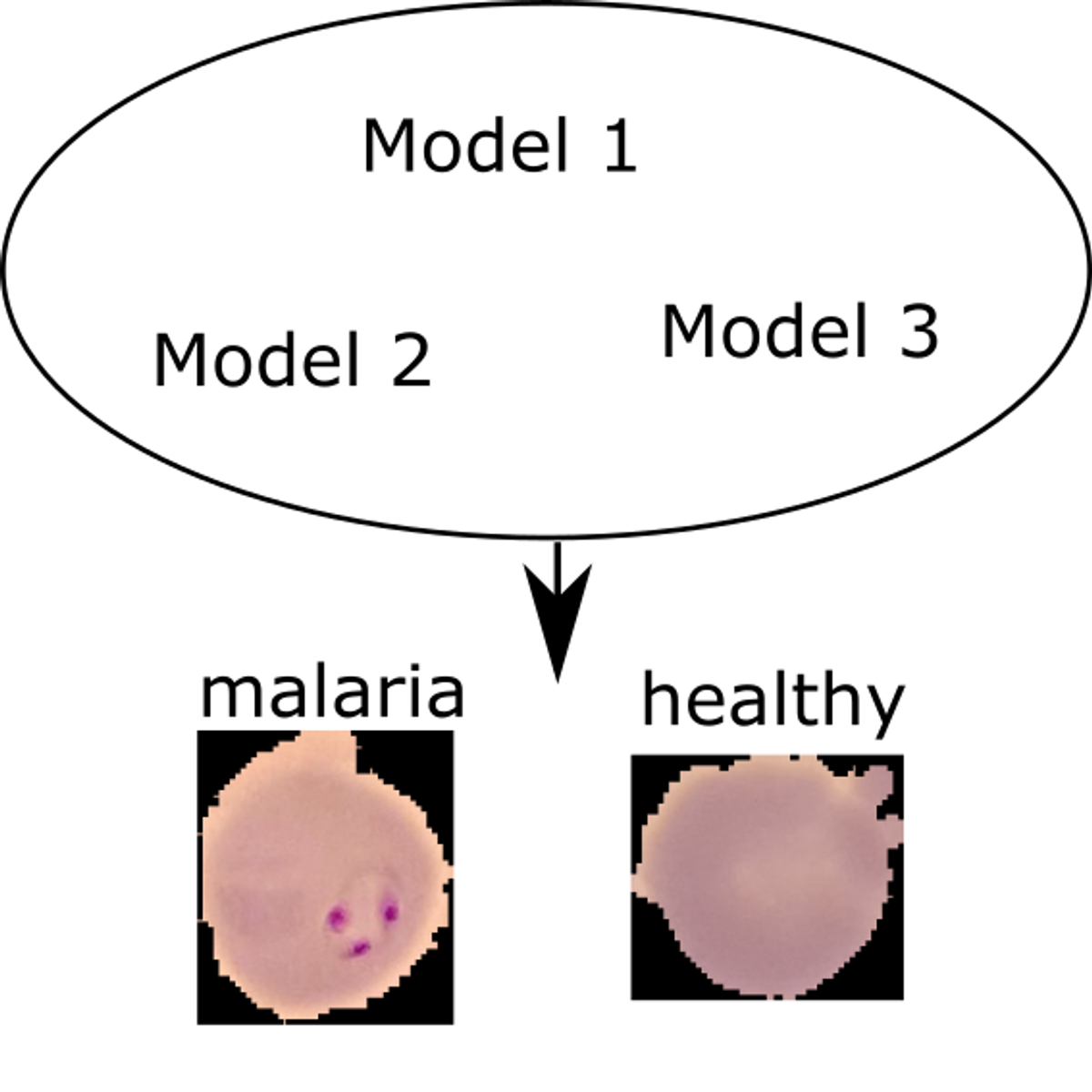
Malaria parasite detection using ensemble learning in Keras
In this 1-hour long project-based course, you will learn what ensemble learning is and how to implement is using python. You will create deep convolutional neural networks using the Keras library to predict the malaria parasite. You will learn various ways of assessing classification models. You will create an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks and apply voting in order to combine the best predictions of your models.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

3D Reconstruction - Multiple Viewpoints
This course focuses on the recovery of the 3D structure of a scene from images taken from different viewpoints. We start by first building a comprehensive geometric model of a camera and then develop a method for finding (calibrating) the internal and external parameters of the camera model. Then, we show how two such calibrated cameras, whose relative positions and orientations are known, can be used to recover the 3D structure of the scene. This is what we refer to as simple binocular stereo. Next, we tackle the problem of uncalibrated stereo where the relative positions and orientations of the two cameras are unknown. Interestingly, just from the two images taken by the cameras, we can both determine the relative positions and orientations of the cameras and then use this information to estimate the 3D structure of the scene.
Next, we focus on the problem of dynamic scenes. Given two images of a scene that includes moving objects, we show how the motion of each point in the image can be computed. This apparent motion of points in the image is called optical flow. Optical flow estimation allows us to track scene points over a video sequence. Next, we consider the video of a scene shot using a moving camera, where the motion of the camera is unknown. We present structure from motion that takes as input tracked features in such a video and determines not only the 3D structure of the scene but also how the camera moves with respect to the scene. The methods we develop in the course are widely used in object modeling, 3D site modeling, robotics, autonomous navigation, virtual reality and augmented reality.
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved


