Back to Courses






Software Development Courses - Page 118
Showing results 1171-1180 of 1266

Build a Modern Computer from First Principles: Nand to Tetris Part II (project-centered course)
In this project-centered course you will build a modern software hierarchy, designed to enable the translation and execution of object-based, high-level languages on a bare-bone computer hardware platform. In particular, you will implement a virtual machine and a compiler for a simple, Java-like programming language, and you will develop a basic operating system that closes gaps between the high-level language and the underlying hardware platform. In the process, you will gain a deep, hands-on understanding of numerous topics in applied computer science, e.g. stack processing, parsing, code generation, and classical algorithms and data structures for memory management, vector graphics, input-output handling, and various other topics that lie at the very core of every modern computer system.
This is a self-contained course: all the knowledge necessary to succeed in the course and build the various systems will be given as part of the learning experience. The only prerequisite is knowledge of programming at the level acquired in introduction to computer science courses. All the software tools and materials that are necessary to complete the course will be supplied freely after you enrol in the course.
This course is accompanied by the textbook "The Elements of Computing Systems" (Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press). While not required for taking the course, the book provides a convenient coverage of all the course topics. The book is available in either hardcopy or ebook form, and MIT Press is offering a 30% discount off the cover price by using the discount code MNTT30 at https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/elements-computing-systems.
The course consists of six modules, each comprising a series of video lectures, and a project. You will need about 2-3 hours to watch each module's lectures, and about 15 hours to complete each one of the six projects. The course can be completed in six weeks, but you are welcome to take it at your own pace. You can watch a TED talk about this course by Googling "nand2tetris TED talk".
*About Project-Centered Courses: Project-centered courses are designed to help you complete a personally meaningful real-world project, with your instructor and a community of learners with similar goals providing guidance and suggestions along the way. By actively applying new concepts as you learn, you’ll master the course content more efficiently; you’ll also get a head start on using the skills you gain to make positive changes in your life and career. When you complete the course, you’ll have a finished project that you’ll be proud to use and share.

Working with AWS S3 Buckets using Python & boto3
In this project, we will look at how to work with the AWS S3, which is Amazon’s File Storage System, programmatically using AWS’s SDK in Python, boto3.
We will first look at how to create and modify AWS S3 Buckets using boto3. We will then look at how to create an S3 Bucket, how to download and upload different types of files to S3. We will then look at how to use Multi-part Transfer to upload large files. We will then move on to how to create Pre-signed URLS to provide temporary Access to users.
We will then learn how to configure bucket policies. And finally look at how to setup CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) which enables client web applications to access our S3 bucket.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Machine Learning Data Lifecycle in Production
In the second course of Machine Learning Engineering for Production Specialization, you will build data pipelines by gathering, cleaning, and validating datasets and assessing data quality; implement feature engineering, transformation, and selection with TensorFlow Extended and get the most predictive power out of your data; and establish the data lifecycle by leveraging data lineage and provenance metadata tools and follow data evolution with enterprise data schemas.
Understanding machine learning and deep learning concepts is essential, but if you’re looking to build an effective AI career, you need production engineering capabilities as well. Machine learning engineering for production combines the foundational concepts of machine learning with the functional expertise of modern software development and engineering roles to help you develop production-ready skills.
Week 1: Collecting, Labeling, and Validating data
Week 2: Feature Engineering, Transformation, and Selection
Week 3: Data Journey and Data Storage
Week 4: Advanced Data Labeling Methods, Data Augmentation, and Preprocessing Different Data Types

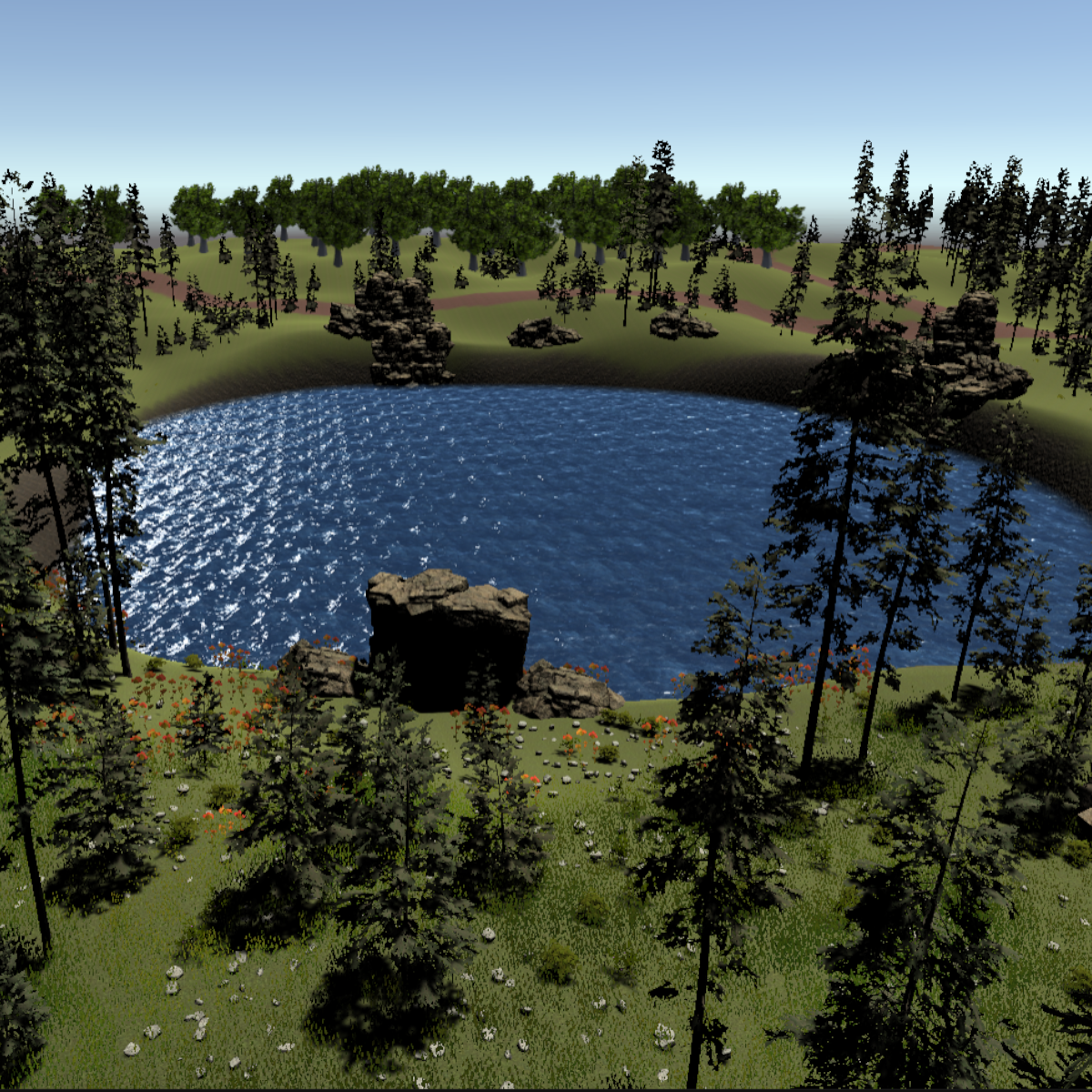
Create Landscapes in Unity Part 3 - Foliage, Rocks, and Lake
In this one-hour, project-based course, you'll learn how to use premade assets to add terrain details to your scene. You'll learn how to paint bushes and flowers using a Paint Detail tool, create a lovely lake with the terrain-paint tool and add a water shader to make your scene more realistic.
The guided project will introduce you to the following Unity concepts:
-Terrain
This is Part 3 of a three-part series on creating landscape settings. Part 1 covers Terrain related settings. Part 2 continues in adding Terrain related objects such as flowers, bushes, and lake. You do not need to do the other parts of the series, but they will help round out your understanding of the topic presented.
Note: This course works best for learners who are based in the North America region. We’re currently working on providing the same experience in other regions.

Build Your First React Website (Part II)
This 1.5 hours guided project is part 2 of the project "Build Your First React Website." In this project, we focus on persistent states for class components and different strategies for them to communicate with each other.
At the end of this course, you will be able to choose and deploy different communication strategies for communications among React components.
This class requires basic React and intermediate to advance experiment in JavaScript development as a prerequisite.

Introduction to Self-Driving Cars
Welcome to Introduction to Self-Driving Cars, the first course in University of Toronto’s Self-Driving Cars Specialization.
This course will introduce you to the terminology, design considerations and safety assessment of self-driving cars. By the end of this course, you will be able to:
- Understand commonly used hardware used for self-driving cars
- Identify the main components of the self-driving software stack
- Program vehicle modelling and control
- Analyze the safety frameworks and current industry practices for vehicle development
For the final project in this course, you will develop control code to navigate a self-driving car around a racetrack in the CARLA simulation environment. You will construct longitudinal and lateral dynamic models for a vehicle and create controllers that regulate speed and path tracking performance using Python. You’ll test the limits of your control design and learn the challenges inherent in driving at the limit of vehicle performance.
This is an advanced course, intended for learners with a background in mechanical engineering, computer and electrical engineering, or robotics. To succeed in this course, you should have programming experience in Python 3.0, familiarity with Linear Algebra (matrices, vectors, matrix multiplication, rank, Eigenvalues and vectors and inverses), Statistics (Gaussian probability distributions), Calculus and Physics (forces, moments, inertia, Newton's Laws).
You will also need certain hardware and software specifications in order to effectively run the CARLA simulator: Windows 7 64-bit (or later) or Ubuntu 16.04 (or later), Quad-core Intel or AMD processor (2.5 GHz or faster), NVIDIA GeForce 470 GTX or AMD Radeon 6870 HD series card or higher, 8 GB RAM, and OpenGL 3 or greater (for Linux computers).

Hands-on Machine Learning with AWS and NVIDIA
Machine learning (ML) projects can be complex, tedious, and time consuming. AWS and NVIDIA solve this challenge with fast, effective, and easy-to-use capabilities for your ML project.
This course is designed for ML practitioners, including data scientists and developers, who have a working knowledge of machine learning workflows. In this course, you will gain hands-on experience on building, training, and deploying scalable machine learning models with Amazon SageMaker and Amazon EC2 instances powered by NVIDIA GPUs. Amazon SageMaker helps data scientists and developers prepare, build, train, and deploy high-quality ML models quickly by bringing together a broad set of capabilities purpose-built for ML. Amazon EC2 instances powered by NVIDIA GPUs along with NVIDIA software offer high performance GPU-optimized instances in the cloud for efficient model training and cost effective model inference hosting.
In this course, you will first get an overview of Amazon SageMaker and NVIDIA GPUs. Then, you will get hands-on, by running a GPU powered Amazon SageMaker notebook instance. You will then learn how to prepare a dataset for model training, build a model, execute model training, and deploy and optimize the ML model. You will also learn, hands-on, how to apply this workflow for computer vision (CV) and natural language processing (NLP) use cases. After completing this course, you will be able to build, train, deploy, and optimize ML workflows with GPU acceleration in Amazon SageMaker and understand the key Amazon SageMaker services applicable to computer vision and NLP ML tasks.

Create AWS EC2 Virtual Machine Using AWS console
In this 1-hour long project-based course, you will learn how to Create an AWS EC2 virtual machine using the AWS console.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud is the service you use to create and run virtual machines (VM), also known as instances. By completing the steps in this guided project, you will successfully launch a Linux VM on Amazon EC2 within the AWS Free Tier. You will also connect to the instance that you launch and then terminate the instance.

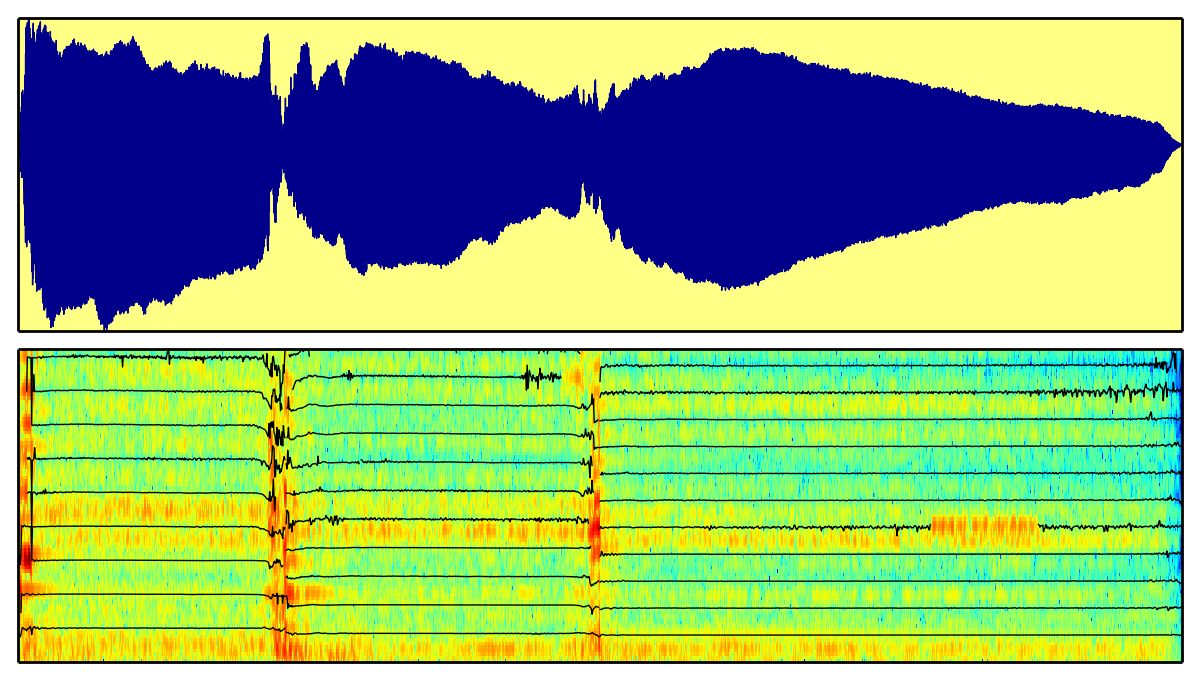
Audio Signal Processing for Music Applications
In this course you will learn about audio signal processing methodologies that are specific for music and of use in real applications. We focus on the spectral processing techniques of relevance for the description and transformation of sounds, developing the basic theoretical and practical knowledge with which to analyze, synthesize, transform and describe audio signals in the context of music applications.
The course is based on open software and content. The demonstrations and programming exercises are done using Python under Ubuntu, and the references and materials for the course come from open online repositories. We are also distributing with open licenses the software and materials developed for the course.

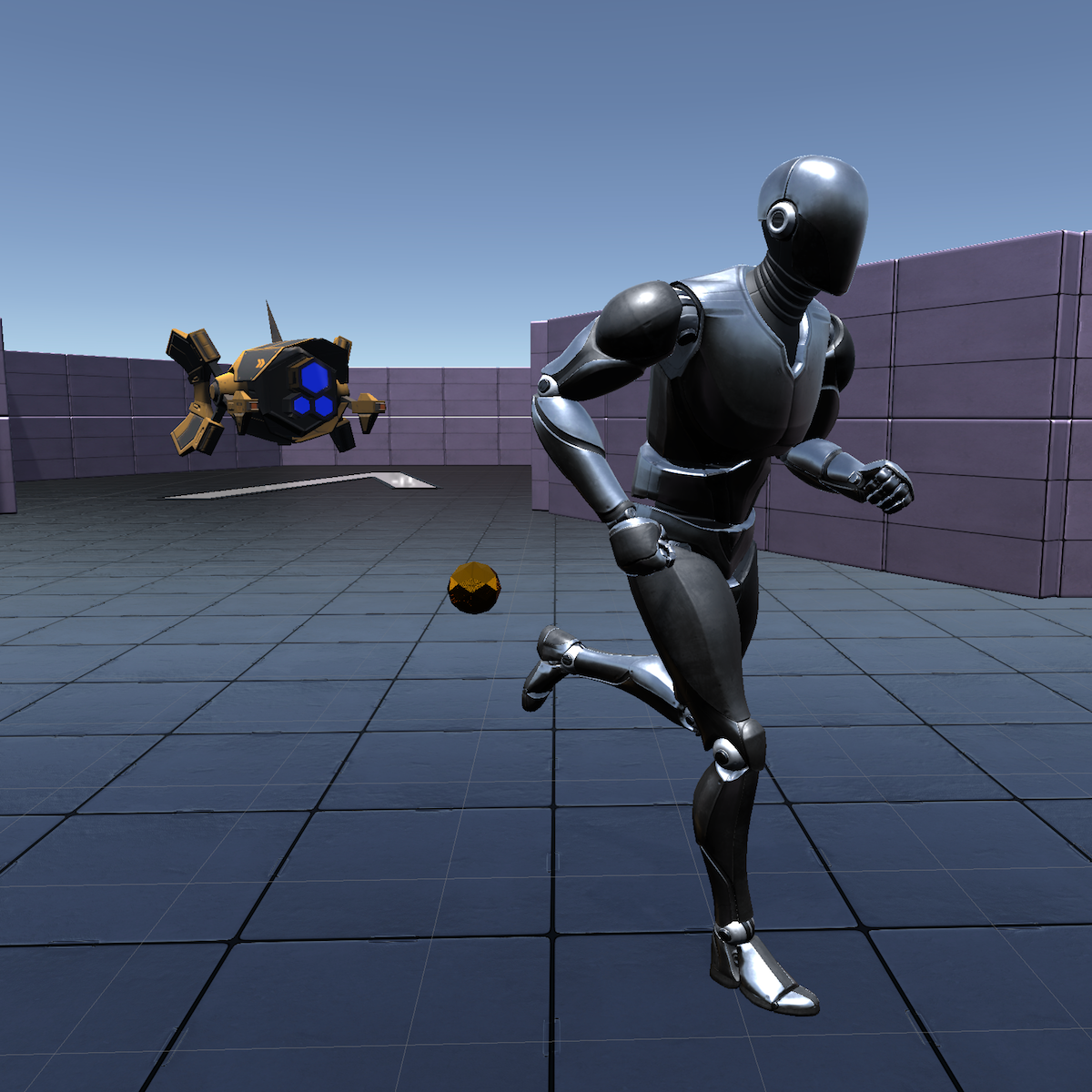
Create Simple Enemy Behaviour with C# in Unity (Intro to AI)
In this one-hour, project-based course, you'll learn how to create a simple enemy behavior tree. You'll learn how to make your enemy characters patrol an area, chase a player in range and attack when it's close enough for melee. You will be able to easily expand the behavior system we create, to add your own conditional behaviors.
To build a behavior tree, this guided project will use and expand upon the following Unity concepts:
- Transform-based movement
- Rigidbody collisions and triggers
- Interfaces
- Events
Consider this guided project to be a "capstone" project for beginners. If you can comfortably complete this course, understand all concepts presented and can reproduce them in your own projects, then congratulations! You have officially graduated to "Intermediate!"
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved


