Back to Courses








Philosophy Courses - Page 2
Showing results 11-20 of 81

Indigenous Religions & Ecology
At first glance the fields of religion and ecology may seem and unlikely pairing, but a deeper consideration reveals the two have a great deal to contribute to one another and are indeed inextricably linked. Religions recognize the unity and interdependence of humans with nature. Ecological sciences affirm this deep interconnection with the natural world. This partnership can inspire work for the wellbeing of the Earth community
There is a need for broader literacy and deeper knowledge of the world’s religions and their ecological contributions. This specialization, "Religions and Ecology: Restoring the Earth Community", contributes such a perspective. Each course celebrates the vitality of religiously-informed action for the Earth and recognizes the longstanding contributions of Indigenous peoples in offering visions and practices for ecological flourishing.
This is course 2 of 5 in the "Religions and Ecology: Restoring the Earth Community" specialization that focuses on the ecological dimensions of religious traditions throughout the world.
The course is designed as a gateway to the significant contributions of Indigenous peoples of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and Pacific Regions for environmental understanding. The diversity of Indigenous communities around the planet makes selective coverage necessary, but shared patterns of resilience manifest themselves worldwide. So much has emerged in the last several decades in understanding traditional environmental knowledge, as you will see.
This course is for lifelong learners curious to know more about world religions and ecology, environmental professionals eager to deepen the discourse of environmental protection and conservation, those working with non-profit organizations and NGOs on issues of ecological justice, and religion leaders and laity who wish to know how they can contribute to interreligious dialogue on environmental projects.

Revolutionary Ideas: Borders, Elections, Constitutions, Prisons
What is the purpose of government? Why should we have a State? What kind of State should we have?
Even within a political community, there may be sharp disagreements about the role and purpose of government. Some want an active, involved government, seeing legal and political institutions as the means to solve our most pressing problems, and to help bring about peace, equality, justice, happiness, and to protect individual liberty. Others want a more minimal government, motivated, perhaps, by some of the disastrous political experiments of the 20th Century, and the thought that political power is often just a step away from tyranny. In many cases, these disagreements arise out of deep philosophical disagreements.
All political and legal institutions are built on foundational ideas. In this course, we will explore those ideas, taking the political institutions and political systems around us not as fixed and unquestionable, but as things to evaluate and, if necessary, to change. We will consider the ideas and arguments of some of the world’s most celebrated philosophers, including historical thinkers such as Plato, Hugo Grotius, David Hume, Thomas Jefferson, and James Madison, and more contemporary theorists such as Michelle Alexander, Kwame Anthony Appiah, Bryan Caplan, Angela Davis, Ronald Dworkin, Jon Elster, John Hart Ely, H.L.A. Hart, Michael Huemer, Andrew Rehfeld, and Jeremy Waldron.
The aim of the course is not to convince you of the correctness of any particular view or political position, but to provide you with a deeper and more philosophically-informed basis for your own views, and, perhaps, to help you better understand the views of those with whom you disagree.
Think Again I: How to Understand Arguments
In this course, you will learn what an argument is. The definition of argument will enable you to identify when speakers are giving arguments and when they are not. Next, you will learn how to break an argument into its essential parts, how to put them in order to reveal their connections, and how to fill in gaps in an argument by adding suppressed premises. By the end of this course, you will be better able to understand and appreciate arguments that you and other people present.
Suggested Readings:
Students who want more detailed explanations or additional exercises or who want to explore these topics in more depth should consult Understanding Arguments: An Introduction to Informal Logic, Ninth Edition, Concise, Chapters 1-5, by Walter Sinnott-Armstrong and Robert Fogelin.
Course Format:
Each week will be divided into multiple video segments that can be viewed separately or in groups. There will be short ungraded quizzes after each segment (to check comprehension) and a longer graded quiz at the end of the course.

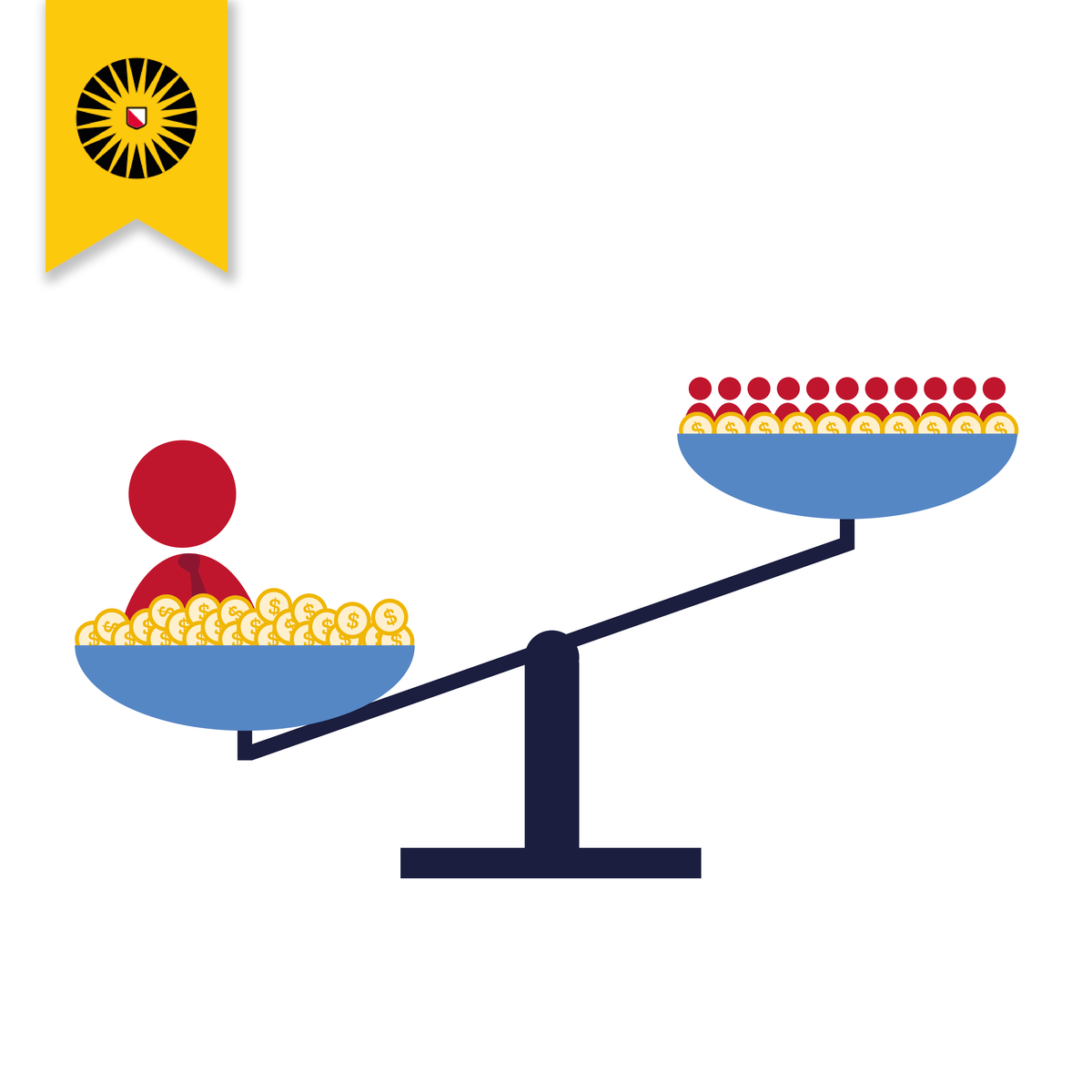
Inequality and Democracy
Most countries are getting more and more unequal. But the core of democracy is political equality: that everyone should have an equal say in how their country is run. Can we really expect these things to go together? Can people have equal political power while economic inequality grows and grows? Take this course and decide for yourself.
You’ll learn about:
• The rise of economic inequality
• Property rights and the corporation
• Democracy: Its value and history
• Campaign finance and lobbying
• Tax avoidance and capital flight
• Alternatives to our economic system
This is an interdisciplinary course combining:
• Politics
• Philosophy
• Economics
• History
• Law
Our course is for anyone looking for an accessible introduction to these topics. You might a concerned citizen, or someone who works in a field like politics, media, education, government or law. The difficulty level is similar to the first-year of an undergraduate degree. No prior knowledge is assumed.

Introduction to Philosophy
This course will introduce you to some of the main areas of research in contemporary philosophy. Each module a different philosopher will talk you through some of the most important questions and issues in their area of expertise. We’ll begin by trying to understand what philosophy is – what are its characteristic aims and methods, and how does it differ from other subjects? Then we’ll spend the rest of the course gaining an introductory overview of several different areas of philosophy.
Topics you’ll learn about will include:
Epistemology, where we’ll consider what our knowledge of the world and ourselves consists in, and how we come to have it;
Philosophy of science, where we’ll investigate foundational conceptual issues in scientific research and practice;
Philosophy of Mind, where we’ll ask questions about what it means for something to have a mind, and how minds should be understood and explained;
Political Philosophy, where we'll investigate whether we have an obligation to obey the law;
Moral Philosophy, where we’ll attempt to understand the nature of our moral judgements and reactions – whether they aim at some objective moral truth, or are mere personal or cultural preferences, and;
Metaphysics, where we’ll think through some fundamental conceptual questions about free will and the nature of reality.
The development of this MOOC has been led by the University of Edinburgh's Eidyn research centre.
To accompany 'Introduction to Philosophy', we are pleased to announce a tie-in book from Routledge entitled 'Philosophy for Everyone'. This course companion to the 'Introduction to Philosophy' course was written by the Edinburgh Philosophy team expressly with the needs of MOOC students in mind. 'Philosophy for Everyone' contains clear and user-friendly chapters, chapter summaries, glossary, study questions, suggestions for further reading and guides to online resources. Please click "Start Here" and navigate to the "Optional Reading" page for more information.

Animals and Institutions
This course explores animals within the context of the functional relationships that sociologists call “institutions.” We first examine the use of animals in laboratory science. We then examine the controversial transformation of animals into “livestock” and "meat." We also explore the perspectives of people committed to rejecting the construction and use of animals as food. Next, we focus on some of the roles of animals in human entertainment with particular attention to dog fighting and zoos. Finally, we investigate animal health and welfare through the lens of dilemmas in veterinary medicine and decisions in animal shelters.

Philosophy and the Sciences: Introduction to the Philosophy of Cognitive Sciences
Course Description
What is our role in the universe as human agents capable of knowledge? What makes us intelligent cognitive agents seemingly endowed with consciousness?
This is the second part of the course 'Philosophy and the Sciences', dedicated to Philosophy of the Cognitive Sciences. Scientific research across the cognitive sciences has raised pressing questions for philosophers. The goal of this course is to introduce you to some of the main areas and topics at the key juncture between philosophy and the cognitive sciences.
Each week we will introduce you to some of these important questions at the forefront of scientific research. We will explain the science behind each topic in a simple, non-technical way, while also addressing the philosophical and conceptual questions arising from it. Areas you’ll learn about will include:
Philosophy of psychology, among whose issues we will cover the evolution of the human mind and the nature of consciousness.
Philosophy of neurosciences, where we’ll consider the nature of human cognition and the relation between mind, machines, and the environment.
Learning objectives
Gain a fairly well-rounded view on selected areas and topics at the intersection of philosophy and the sciences
Understand some key questions, and conceptual problems arising in the cognitive sciences.
Develop critical skills to evaluate and assess these problems.
Suggested Readings
To accompany 'Philosophy and the Sciences', we are pleased to announce a tie-in book from Routledge entitled 'Philosophy and the Sciences for Everyone'. This course companion to the 'Philosophy and the Sciences' course was written by the Edinburgh Philosophy and the Sciences team expressly with the needs of MOOC students in mind. 'Philosophy and the Sciences for Everyone' contains clear and user-friendly chapters, chapter summaries, glossary, study questions, suggestions for further reading and guides to online resources.
Please note, this companion book is optional - all the resources needed to complete the course are available freely and listed on the course site.

Social Norms, Social Change II
This course is Part 2 of the Social Norms, Social Change series. In this course, we will examine social change, the tools we may use to enact change, and put into practice all we have learned in Part 1. See Social Norms, Social Change Part I at this link: https://coursera.org/learn/norms
This course covers scripts and schemas, the cognitive structures in which social expectations are embedded, and their relationship with social norms. The course then examines the essentials of norm abandonment, including the relations between personal beliefs and social expectations. We will also evaluate existing intervention strategies, including legal reforms, information campaigns, economic incentives, and group deliberations. Finally, we look at a variety of tools policy makers may use to effect change, highlight the role of trendsetters in social change, and explore the conditions under which they can be successful. The course is a joint Penn-UNICEF project."
Please see the following link for a 30% discount on the book that accompanies this course:
https://global.oup.com/academic/product/9780190622053/?cc=us&lang=en&promocode=AAFLYG6

Primate Conservation
We are presently facing a potential extinction crisis for the order Primates (and many other life forms). In this course we will learn about threats to primate conservation globally. We will be using the, “Primates in Peril: The World’s 25 Most Endangered Primates 2018-2020” by Schwitzer et al. (2019) as a basis for the discussion of global primate populations. We will investigate conservation status, threats to conservations, success and failures within protecting our closest evolutionary cousins.
Think Again II: How to Reason Deductively
Deductive arguments are supposed to be valid in the sense that the premises guarantee that the conclusion is true. In this course, you will learn how to use truth-tables and Venn diagrams to represent the information contained in the premises and conclusion of an argument so that you can determine whether or not the argument is deductively valid.
Suggested Readings:
Students who want more detailed explanations or additional exercises or who want to explore these topics in more depth should consult Understanding Arguments: An Introduction to Informal Logic, Ninth Edition, Concise, Chapters 6 and 7 by Walter Sinnott-Armstrong and Robert Fogelin.
Course Format:
Each week will be divided into multiple video segments that can be viewed separately or in groups. There will be short ungraded quizzes after each segment (to check comprehension) and a longer graded quiz at the end of the course.
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Find Jobs & Internships
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved