Back to Courses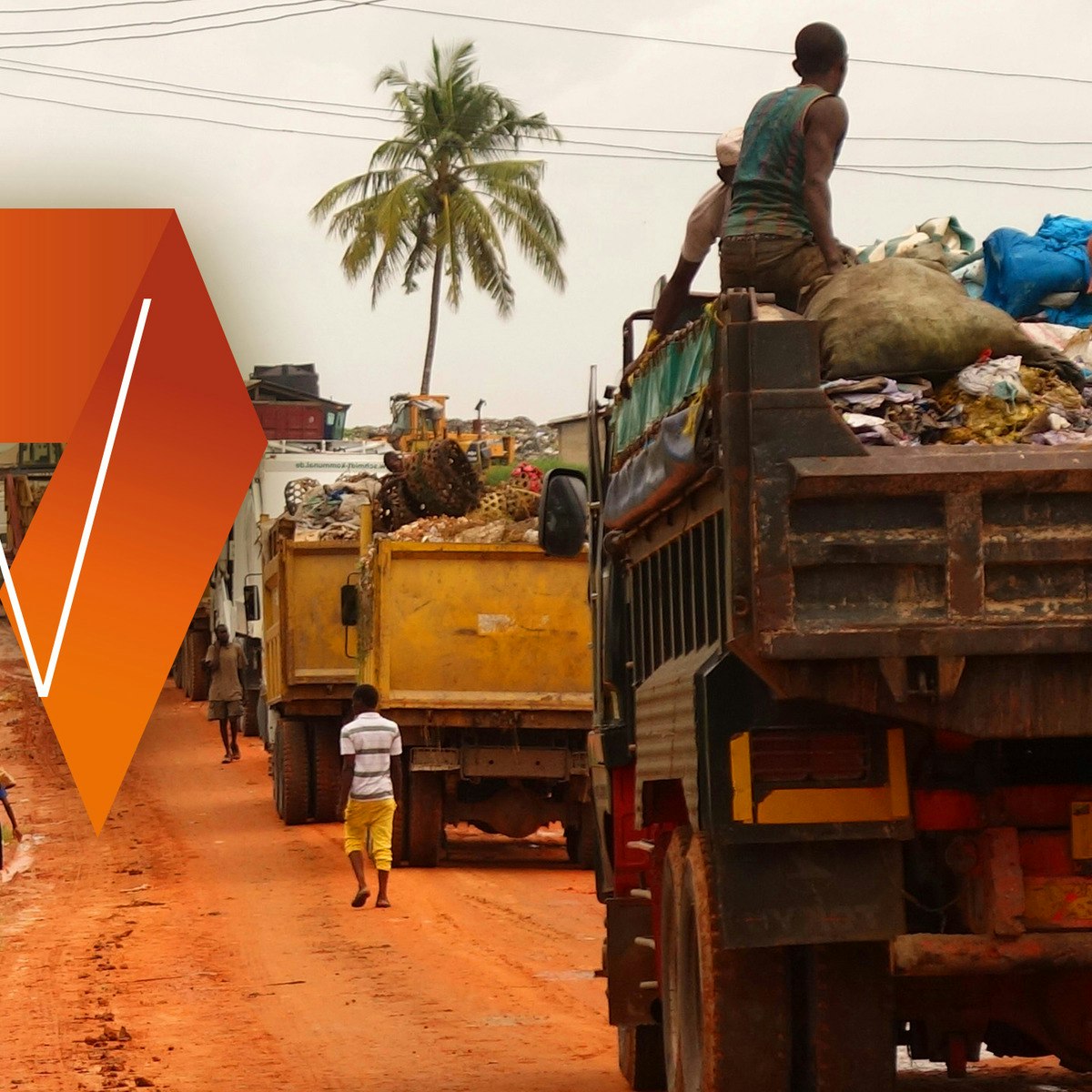








Environmental Science And Sustainability Courses
Showing results 1-10 of 151

Municipal Solid Waste Management in Developing Countries
Have you come across large piles of garbage in neighbourhoods and streets and smelly waste disposal sites polluting the environment of low- and middle-income countries? Do you want to know what kind of sustainable solutions are appropriate to better manage waste and enhance recycling and recovery? If yes, this course is for you!
This course provides you with an overview of the municipal solid waste management situation in low- and middle-income countries. It covers key elements of the waste management system, such as its technical, environmental, social, financial and institutional aspects. Besides understanding the challenges, you will be introduced to appropriate and already applied solutions through selected case studies.

Greening the Economy: Sustainable Cities
How can we shape our urban development towards sustainable and prosperous futures?
This course explores sustainable cities as engines for greening the economy in Europe and around the world. We place cities in the context of sustainable urban transformation and climate change. We connect the key trends of urbanization, decarbonisation and sustainability. We examine how visions, experiments and innovations can transform urban areas. And we look at practices (what is happening in cities at present) and opportunities (what are the possibilities for cities going forwards into the future).
This course was launched in January 2016, and it was updated in September 2021 with new podcasts, films and publications. The course is produced by Lund University in cooperation with WWF and ICLEI – Local Governments for Sustainability who work with creating sustainable cities. The course features researchers, practitioners and entrepreneurs from a range organisations.

Our Energy Future
This course is designed to introduce students to the issues of energy in the 21st century – including food and fuels – which are inseparably linked – and will discuss energy production and utilization from the biology, engineering, economics, climate science, and social science perspectives.
This course will cover the current production and utilization of energy, as well as the consequences of this use, examining finite fossil energy reserves, how food and energy are linked, impacts on the environment and climate, and the social and economic impacts of our present energy and food production and use. After the introductory lectures, we will examine the emerging field of sustainable energy, fuel and food production, emphasizing the importance of developing energy efficient and sustainable methods of production, and how these new technologies can contribute to replacing the diminishing supplies of fossil fuels, and reduce the consequences of carbon dioxide release into the environment. This course will also cover the importance of creating a sustainable energy future for all societies including those of the developing world. Lectures will be prepared and delivered by leading UC San Diego and Scripps Institution of Oceanography faculty and industry professionals across these areas of expertise.

GIS Data Formats, Design and Quality
In this course, the second in the Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Specialization, you will go in-depth with common data types (such as raster and vector data), structures, quality and storage during four week-long modules:
Week 1: Learn about data models and formats, including a full understanding of vector data and raster concepts. You will also learn about the implications of a data’s scale and how to load layers from web services.
Week 2: Create a vector data model by using vector attribute tables, writing query strings, defining queries, and adding and calculating fields. You'll also learn how to create new data through the process of digitizing and you'll use the built-in Editor tools in ArcGIS.
Week 3: Learn about common data storage mechanisms within GIS, including geodatabases and shapefiles. Learn how to choose between them for your projects and how to optimize them for speed and size. You'll also work with rasters for the first time, using digital elevation models and creating slope and distance analysis products.
Week 4: Explore datasets and assess them for quality and uncertainty. You will also learn how to bring your maps and data to the Internet and create web maps quickly with ArcGIS Online.
Take GIS Data Formats, Design and Quality as a standalone course or as part of the Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Specialization. You should have equivalent experience to completing the first course in this specialization, Fundamentals of GIS, before taking this course. By completing the second class in the Specialization you will gain the skills needed to succeed in the full program.

Introduction to Biology: Ecology
Ecology is all about connections. In this course, we’ll see how interdependent every living thing is and how people are impacting the natural world. Like all sciences, ecology isn’t just a list of known facts– it’s also a process. I love telling stories, and I’ve included many stories about how we’ve come to know what we know about ecology through observations and experiments.

Renewable Energy Technology Fundamentals
Renewable energy is one of the fastest growing industries on the planet, with billions of dollars invested each year to meet international energy sustainability goals. This course will provide you with a solid foundation for understanding and deploying important renewable energy technologies such as wind and solar. In addition, you will come away with a good understanding of important energy storage technologies such as pumped hydro, batteries, and hydrogen.
Upon completing the course, you will be conversant with the opportunities and challenges of renewable energy technologies. You will be comfortable participating in debates and making decisions regarding these technologies. And the knowledge you gain will be foundational for further study of renewable power systems, renewable energy projects, and forecasts for the future of renewable energy. We hope you will join us on our journey!
This course is the first in a four-course Coursera specialization in Renewable Energy.
• Renewable Energy Technology Fundamentals
• Renewable Power & Electricity Systems
• Renewable Energy Projects
• Renewable Energy Futures
Course logo image credit: "Wind Turbine" icon courtesy of Vectors Point from the Noun Project.

Fundamentals of Fluid-Solid Interactions
What is fluid-solid interactions ? It is what happens when the motions of a fluid and of a solid are somehow coupled. This happens all the time, around you when leaves flutter in the wind, inside you when your heart beats, above you when wings of a plane vibrate, under the sea... The idea behind this MOOC is to give you the basic tools to be able to predict and eventually mitigate things called flutter, galloping, sloshing, vortex-induced vibrations, added mass, to cite a few.
We are going to consider any possible domains of applications such as civil engineering, aerospace engineering, nuclear engineering , ocean engineering, biomechanics and even food processing !
This is why we called the course “Fundamentals of Fluid Solid Interactions ”. There are so many phenomena and so many models that we need to work together on the basic mechanisms .
If you want to see how fluid-solid interactions work, and be able to use that knowledge, join us !
A first session of the course was run in early 2016, with learners from over 100 countries. It is now available with subtitles, in English and now in Chinese.
See the video at http://goo.gl/YKSMnD

Sustainable Transportation Networks and Streetscapes
This course will evaluate best practices in transportation networks, thoroughfares, and streetscape designs for the effective movement of people, goods, and services in a region. Sustainable public and private streetscape design and application will be reviewed and evaluated for applications for sustainable cities. Considerations are assessed for smart urban planning, growth, and lifestyle. Strategies for creating equitable, healthy, and sustainable communities are also evaluated.
By the end of this course, you will be able to:
1. Survey and evaluate thoroughfare network considerations for connectivity, block size and sidewalk interaction.
2. Compare different complete street design options for application in smart growth planning.
3. Evaluate sidewalk design and planning strategies for public and private sidewalks to include street tree configurations and street light design.
4. Examine issues of water management with specialized curb design, ground water recharge areas and swales as part of the streetscape design and planning.
5. Identify and evaluate the differences between free-flow, slow-flow, and yield-flow thoroughfare design concepts.
6. Assess and evaluate smart urban planning, growth, and lifestyle indicators.
The target audience for this course includes:
- Government Officials involved planning, designing, monitoring, enforcement, and assessment of sustainable project developments at the local, state, and federal level.
- Private sector companies in the transportation and municipal design and construction business
- Architects interested in advancing sustainable concepts for cities and communities
- Foundations, associations, and other NGOs that support smart growth strategies
- Academic faculty and students studying and researching community sustainability and resilience
- Private citizens interested in improving their communities and living conditions

Large Marine Ecosystems: Assessment and Management
Focusing on the Large Marine Ecosystems (LMEs) of the world, this course will introduce the concept and practice of ecosystem-based management. LMEs occupy areas of coastal ocean at least 200 000 km² or greater in size. These coastal waters produce 12.6 trillion USD in ecosystem goods and services annually and are vitally important for billions of people around the globe.
Because LMEs are bounded by ocean features and are globally linked, management of human activities needs to occur in an integrated fashion across political boundaries and economic sectors (e.g. fishing, shipping, energy, tourism, and mining.) This represents a new type of management approached - shifting from single sector-based to multi-sector assessment and management within the spatial domain of the world's 66 Large Marine Ecosystems. There is global high-level support for this new approach and in this course, we will introduce the concepts and tools for assessing and managing LMEs.
Together, leaders and experts in a global movement to recover and sustain the goods and services of LMEs will introduce you to the mechanisms used for assessment (Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis), planning and implementation (Strategic Action Programme). Based on recent activities in implementation and practice of the LME approach in 22 projects around the globe, we will showcase examples of effective management at this scale, and highlight the challenges and issues. By the end of the online course, we hope you will be able to actively use this knowledge to advance sustainable development of the world’s oceans.
The course was created with the support and input of: the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), UNESCO-IOC and IW:LEARN.

Climate Change and Water in Mountains: A Global Concern
What is climate change ? How are mountain regions affected by the evolution of water resources and their uses ? What kind of risks need to be considered ?
Mountains are recognized as particularly sensitive physical environments where intense and rapid changes have in the past, and may increasingly in the future, place pressure on their resource base.
In this context, a team of roughly 100 experts worked from 2008 to 2013 for the European ACQWA project (www.acqwa.ch) which was coordinated by the University of Geneva. The primary objectives of the project were to assess the impacts of a changing climate on the quantity and quality of water originating in mountain regions, particularly where snow- and ice melt represent a large, sometimes the largest, streamflow component. A further objective of the project was to determine the potential disruptions to water-dependent economic activities related to the climate impacts on hydrological systems, and to propose a portfolio of possible adaptation strategies.
This particular MOOC is inspired by the ACQWA Project and offers a better understanding of climate change, its impacts on the quality and quantity of water in mountain regions and the risks related to changing water resources. From an interdisciplinary perspective, the participation of twenty-five instructors from five different countries (Switzerland, England, South Korea, India and Nepal) and fourteen institutions (UNIGE, RTS, UNIFR, UZH, ETHZ, Meteodat GmbH, WGMS, Imperial College London, Agroscope, République et Canton de Genève, Yonsei University, IHCAP, ICIMOD, SDC, FOEN) highlights the diversity of both theoretical and practical viewpoints related to these issues.
By the end of this course, you will be able :
- to define the general concept of climate change in mountain regions
- to understand the concepts associated with climate change such as adaptation and water governance strategies
- to consider the impacts of climate change on water resources in mountain regions
- to identify the impacts of climate change on hydropower, agriculture, aquatic ecosystems and health
- to enumerate risks that can occur in mountain areas and lead to disruptions in water availability and use.
Your acquired knowledge will be evaluated through multiple-choice quizzes at the end of each unit of the course.
This MOOC on “Climate Change and Water in Mountain Regions : A Global Concern” was initiated and financed by the University of Geneva, through its Institute for Environmental Sciences.
We look forward to you joining us !
Popular Internships and Jobs by Categories
Find Jobs & Internships
Browse
© 2024 BoostGrad | All rights reserved